Metal- Pseudomonas veronii 2E Interactions as Strategies for Innovative Process Developments in Environmental Biotechnology
- PMID: 33746918
- PMCID: PMC7965972
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.622600
Metal- Pseudomonas veronii 2E Interactions as Strategies for Innovative Process Developments in Environmental Biotechnology
Abstract
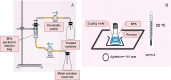
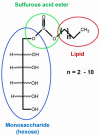
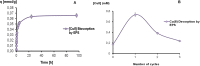
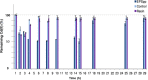
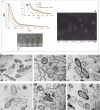
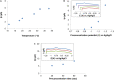
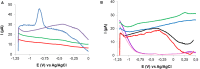
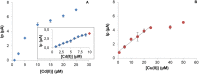
The increase of industrial discharges is the first cause of the contamination of water bodies. The bacterial survival strategies contribute to the equilibrium restoration of ecosystems being useful tools for the development of innovative environmental biotechnologies. The aim of this work was to study the Cu(II) and Cd(II) biosensing, removal and recovery, mediated by whole cells, exopolymeric substances (EPS) and biosurfactants of the indigenous and non-pathogenic Pseudomonas veronii 2E to be applied in the development of wastewater biotreatments. An electrochemical biosensor was developed using P. veronii 2E biosorption mechanism mediated by the cell surface associated to bound exopolymeric substances. A Carbon Paste Electrode modified with P. veronii 2E (CPEM) was built using mineral oil, pre-washed graphite power and 24 h-dried cells. For Cd(II) quantification the CPEM was immersed in Cd(II) (1-25 μM), detected by Square Wave Voltammetry. A similar procedure was used for 1-50 μM Cu(II). Regarding Cd(II), removal mediated by immobilized EPS was tested in a 50 ml bioreactor with 0.13 mM Cd(II), pH 7.5. A 54% metal retention by EPS was achieved after 7 h of continuous operation, while a 40% was removed by a control resin. In addition, surfactants produced by P. veronii 2E were studied for recovery of Cd(II) adsorbed on diatomite, obtaining a 36% desorption efficiency at pH 6.5. Cu(II) adsorption from a 1 mM solution was tested using P. veronii 2E purified soluble EPS in 50 mL- batch reactors (pH = 5.5, 32°C). An 80% of the initial Cu(II) was retained using 1.04 g immobilized EPS. Focusing on metal recovery, Cu nanoparticles (NPs) biosynthesis by P. veronii 2E was carried out in Cu(II)-PYG Broth at 25°C for 5 days. Extracellular CuNPs were characterized by UV-Vis spectral analysis while both extracellular and intracellular NPs were analyzed by SEM and TEM techniques. Responses of P. veronii 2E and its products as biosurfactants, bound and soluble EPS allowed Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal, recovery and biosensing resulting in a multiple and versatile tool for sustainable wastewater biotreatments.
Keywords: Cu nanoparticles; Pseudomonas veronii; biosensor; biosurfactant; exopolymeric substances; metal removal and recovery.
Copyright © 2021 Busnelli, Lazzarini Behrmann, Ferreira, Candal, Ramirez and Vullo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infrared spectroscopy with multivariate analysis to interrogate the interaction of whole cells and secreted soluble exopolimeric substances of Pseudomonas veronii 2E with Cd(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II).Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Mar 5;228:117820. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.117820. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 31771908
-
Immobilization of exopolymeric substances from bacteria for metal removal: A study on characterization, optimization, reusability and toxicity.J Environ Manage. 2022 Dec 1;323:116244. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116244. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Environ Manage. 2022. PMID: 36116257
-
Cadmium, zinc and copper biosorption mediated by Pseudomonas veronii 2E.Bioresour Technol. 2008 Sep;99(13):5574-81. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.060. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Bioresour Technol. 2008. PMID: 18158237
-
Chemical characterization and ligand behaviour of Pseudomonas veronii 2E siderophores.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug 17;34(9):134. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2519-3. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30120613
-
Extracellular polymeric substances of bacteria and their potential environmental applications.J Environ Manage. 2014 Nov 1;144:1-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.05.010. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Environ Manage. 2014. PMID: 24907407 Review.
Cited by
-
Orally Administrated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BGAN8-Derived EPS-AN8 Ameliorates Cd Hazards in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2845. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032845. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769176 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Exopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas in Heavy Metal Removal and Other Remediation Strategies.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Oct 11;14(20):4253. doi: 10.3390/polym14204253. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Interactive Effects Provided by an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Yeast on the Growth of Oenothera picensis Established on Cu Mine Tailings.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;12(23):4012. doi: 10.3390/plants12234012. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aglan R. F., Hamed M. M., Saleh H. M. (2019). Selective and sensitive determination of Cd(II) ions in various samples using a novel modified carbon paste electrode. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 10:7. 10.1186/s40543-019-0166-4 - DOI
-
- Akyilmaz E., Canbay E., Dinçkaya E., Güvenç C., Yaşa İ, Bayram E. (2017). Simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine by using Candida tropicalis yeast cells immobilized in a carbon paste electrode modified with single wall carbon nanotube. Electroanalysis 29 1976–1984. 10.1002/elan.201700125 - DOI
-
- Alpat Ş, Alpat S. K., Çadirci B. H., Yaşa I., Telefoncu A. (2008). A novel microbial biosensor based on Circinella Sp. modified carbon paste electrode and its voltammetric application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 134 175–181. 10.1016/j.snb.2008.04.044 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

