Genetic Susceptibility to Joint Occurrence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: How Far Is Our Understanding?
- PMID: 33746952
- PMCID: PMC7968419
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.606620
Genetic Susceptibility to Joint Occurrence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: How Far Is Our Understanding?
Abstract
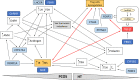
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) are endocrine disorders that commonly occur among young women. A higher prevalence of HT in women with PCOS, relative to healthy individuals, is observed consistently. Combined occurrence of both diseases is associated with a higher risk of severe metabolic and reproductive complications. Genetic factors strongly impact the pathogenesis of both PCOS and HT and several susceptibility loci associated with a higher risk of both disorders have been identified. Furthermore, some candidate gene polymorphisms are thought to be functionally relevant; however, few genetic variants are proposed to be causally associated with the incidence of both disorders together.
Keywords: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; association studies; autoimmune thyroid disease; genetic variants; polycystic ovary syndrome; susceptibility loci.
Copyright © 2021 Zeber-Lubecka and Hennig.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

