Roles of the Dynamic Tumor Immune Microenvironment in the Individualized Treatment of Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33746989
- PMCID: PMC7970116
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653358
Roles of the Dynamic Tumor Immune Microenvironment in the Individualized Treatment of Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
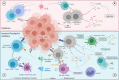
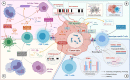
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are currently a first-line treatment option for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). However, recent clinical studies have shown that a large number of patients do not respond to ICIs. Moreover, only a few patients achieve a stable and durable response even with combination therapy based on ICIs. Available studies have concluded that the response to immunotherapy and targeted therapy in patients with ccRCC is affected by the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME), which can be manipulated by targeted therapy and tumor genomic characteristics. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the dynamic nature of the TIME is important for improving the efficacy of immunotherapy or combination therapy in patients with advanced ccRCC. Here, we explore the possible mechanisms by which the TIME affects the efficacy of immunotherapy and targeted therapy, as well as the factors that drive dynamic changes in the TIME in ccRCC, including the immunomodulatory effect of targeted therapy and genomic changes. We also describe the progress on novel therapeutic modalities for advanced ccRCC based on the TIME. Overall, this review provides valuable information on the optimization of combination therapy and development of individualized therapy for advanced ccRCC.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; genomic characteristics; immunotherapy; targeted therapy; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Xie, Tian, Liu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

