Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma: Diagnosis, management and prognosis
- PMID: 33747211
- PMCID: PMC7967932
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12615
Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma: Diagnosis, management and prognosis
Abstract
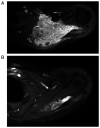
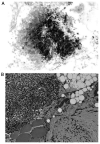
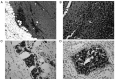
Extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma (EES) is a relatively uncommon primary tumor of the soft tissues, which accounts for 20-30% of all reported cases of ES. Being uncommon, all members of the ES family tumors are treated following the same general protocol of sarcoma tumors. The present review summarizes the diagnosis, management and prognosis of EES, focusing on the differences between the subtypes of ESS. The clinical features and imaging of EES are also discussed. Magnetic resonance imaging is the modality of choice for diagnostic imaging and local staging, while core-needle biopsy with pathological testing is used to obtain a definitive diagnosis. Although several oncology groups endorse that ES family of tumors should be treated with similar algorithm and protocols, some studies have demonstrated that surgery and radiotherapy may be used as a form of local control. However, further studies are required to conclude the optimum treatment option for EES.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; diagnosis; prognosis; therapy.
Copyright © 2021, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Peabody TD, Attar S, editors. Cancer Treatment and Research, Cham. Springer International Publishing; Imprint, Springer, Berlin, Germay: 2014. SpringerLink: Orthopaedic Oncology: Primary and metastatic tumors of the skeletal system; pp. 203–223.
-
- Carpentieri DF, Qualman SJ, Bowen J, Krausz T, Marchevsky A, Dickman PS, Cancer Committee, College of American Pathologists Protocol for the examination of specimens from pediatric and adult patients with osseous and extraosseous Ewing sarcoma family of tumors, including peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor and Ewing sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2005;129:866–873. doi: 10.5858/2005-129-866-PFTEOS. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
