Development of a ghrelin receptor inverse agonist for positron emission tomography
- PMID: 33747360
- PMCID: PMC7939532
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27895
Development of a ghrelin receptor inverse agonist for positron emission tomography
Abstract
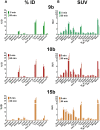
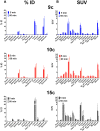
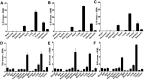
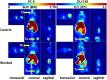
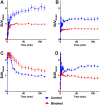
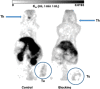
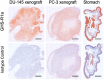
Imaging of Ghrelin receptors in vivo provides unique potential to gain deeper understanding on Ghrelin and its receptors in health and disease, in particular, in cancer. Ghrelin, an octanoylated 28-mer peptide hormone activates the constitutively active growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a (GHS-R1a) with nanomolar activity. We developed novel compounds, derived from the potent inverse agonist K-(D-1-Nal)-FwLL-NH2 but structurally varied by lysine conjugation with 1,4,7-triazacyclononane,1-glutaric acid-4,7-acetic acid (NODAGA), palmitic acid and/or diethylene glycol (PEG2) to allow radiolabeling and improve pharmacokinetics, respectively. All compounds were tested for receptor binding, potency and efficacy in vitro, for biodistribution and -kinetics in rats and in preclinical prostate cancer models on mice. Radiolabeling with Cu-64 and Ga-68 was successfully achieved. The Cu-64- or Ga-68-NODAGA-NH-K-K-(D-1-NaI)-F-w-L-L-NH2 radiotracer were specifically accumulated by the GHS-R1a in xenotransplanted human prostate tumor models (PC-3, DU-145) in mice. The tumors were clearly delineated by PET. The radiotracer uptake was also partially blocked by K-(D-1-Nal)-FwLL-NH2 in stomach and thyroid. The presence of the GHS-R1a was also confirmed by immunohistology. In the arterial rat blood plasma, only the original compounds were found. The Cu-64 or Ga-68-NODAGA-NH-K-K-(D-1-NaI)-F-w-L-L-NH2 radiolabeled inverse agonists turned out to be potent and safe. Due to their easy synthesis, high affinity, medium potency, metabolic stability, and the suitable pharmacokinetic profiles, they are excellent tools for imaging and quantitation of GHS-R1a expression in normal and cancer tissues by PET. These compounds can be used as novel biomarkers of the Ghrelin system in precision medicine.
Keywords: cancer; copper-64; growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R); prostate cancer; small animal imaging.
Copyright: © 2021 Bergmann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Liu H, Luo J, Guillory B, Chen JA, Zang P, Yoeli JK, Hernandez Y, Lee II, Anderson B, Storie M, Tewnion A, Garcia JM. Ghrelin ameliorates tumor-induced adipose tissue atrophy and inflammation via Ghrelin receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Oncotarget. 2020; 11:3286–302. 10.18632/oncotarget.27705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

