On-Chip Biogenesis of Circulating NK Cell-Derived Exosomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Exhibits Antitumoral Activity
- PMID: 33747745
- PMCID: PMC7967048
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202003747
On-Chip Biogenesis of Circulating NK Cell-Derived Exosomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Exhibits Antitumoral Activity
Abstract
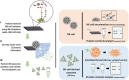
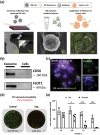
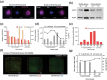
As the recognition between natural killer (NK) cells and cancer cells does not require antigen presentation, NK cells are being actively studied for use in adoptive cell therapies in the rapidly evolving armamentarium of cancer immunotherapy. In addition to utilizing NK cells, recent studies have shown that exosomes derived from NK cells also exhibit antitumor properties. Furthermore, these NK cell-derived exosomes exhibit higher stability, greater modification potentials and less immunogenicity compared to NK cells. Therefore, technologies that allow highly sensitive and specific isolation of NK cells and NK cell-derived exosomes can enable personalized NK-mediated cancer therapeutics in the future. Here, a novel microfluidic system to collect patient-specific NK cells and on-chip biogenesis of NK-exosomes is proposed. In a small cohort of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, both NK cells and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were isolated, and it is found NSCLC patients have high numbers of NK and NK-exosomes compared with healthy donors, and these concentrations show a trend of positive and negative correlations with bloodborne CTC numbers, respectively. It is further demonstrated that the NK-exosomes harvested from NK-graphene oxide chip exhibit cytotoxic effect on CTCs. This versatile system is expected to be used for patient-specific NK-based immunotherapies along with CTCs for potential prognostic/diagnostic applications.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; circulating tumor cells; exosome biogenesis; microfluidics; natural killer cells.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
S.N. is one of the named inventors on a patent for Microfluidic Labyrinth Technology granted to the University of Michigan. S.N. is also the co‐founder of Labyrinth Biotech Inc. The funders and the company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
