Computational fluid dynamics modeling aiding surgical planning in a toddler with Parkes Weber syndrome
- PMID: 33747785
- PMCID: PMC7978412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.epsc.2021.101780
Computational fluid dynamics modeling aiding surgical planning in a toddler with Parkes Weber syndrome
Abstract
Parkes Weber syndrome is a fast-flow and slow-flow vascular anomaly with limb overgrowth that can lead to congestive heart failure and limb ischemia. Current management strategies have focused on symptom management with focal embolization. A pediatric case with early onset heart failure is reported. We discuss the use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling to guide a surgical management strategy in a toddler with an MAP2K1 mutation.
Keywords: Arterial banding; Computational fluid dynamics modeling; Congestive heart failure; MAP2K1 mutation; Parkes Weber syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

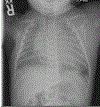


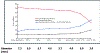
References
-
- Branzic I, et al. Parkes Weber syndrome—diagnostic and management paradigms: a systematic review. Phlebology 2017;32(6):371–83. - PubMed
-
- Parkes Weber F, Liang MG. Angioma: formation in connection with hypertrophy of limbs and hemi-hypertrophy. Br J Dermatol 1907;19:231–5.
-
- Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Vikkula M. RASA1: variable phenotype with capillary and arteriovenous malformations. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2005;15:265–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
