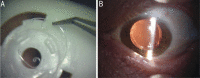
Comparative evaluation of rotational stability of toric IOLs with four-eyelet vs two-eyelet capsular tension rings in eyes with high myopia
- PMID: 33747812
- PMCID: PMC7930546
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2021.03.07
Comparative evaluation of rotational stability of toric IOLs with four-eyelet vs two-eyelet capsular tension rings in eyes with high myopia
Abstract
Aim: To compare the rotational stability of Toric intraocular lens (IOLs) implantation combined with four-eyelet or two-eyelet capsular tension rings (CTRs) in eyes with high myopia and cataract.
Methods: This prospective randomized controlled interventional study included 33 eyes which had preoperative corneal astigmatism ≥1.5 D and ocular axial length ≥25.5 mm. These eyes were randomly divided into two groups to undergo phacoemulsification and toric IOL implantation with either four-eyelet CTR implantation (group A, n=16) or two-eyelet CTR implantation (group B, n=17). Uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA), best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), phoropter examination results, and toric IOL rotation degrees were tested 6mo after the surgery.
Results: In both groups, the toric IOL was in the capsular sac 6mo after surgery. The difference between the two groups in terms of visual outcome was not found to be statistically significant (P>0.05) at a follow-up of 6mo. The mean residual astigmatism values were 0.56±0.22 D and 0.92±0.24 D in A and B groups, respectively (P<0.001). The mean rotation degree of IOL was 1.00°±0.73° in group A and 3.53°±1.46° in group B (P<0.001).
Conclusion: In cataract patients with high myopia and astigmatism, four-eyelet CTR can effectively increase the rotation stability of toric IOLs, achieving the desired goal of correcting corneal astigmatism.
Keywords: axial myopic astigmatism; capsular tension ring; cataract; toric intraocular lens.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propensity-matched comparison of postoperative stability and visual outcomes of toric intraocular lens with or without a capsular tension ring and updated meta-analysis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;261(4):989-998. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05851-y. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36201025
-
Combined Special Capsular Tension Ring and Toric IOL Implantation for Management of Astigmatism and High Axial Myopia with Cataracts.Semin Ophthalmol. 2018;33(3):389-394. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2016.1247181. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Semin Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 28005433
-
Effect of Capsular Tension Ring Implantation on Postoperative Rotational Stability of a Toric Intraocular Lens.J Refract Surg. 2020 Mar 1;36(3):186-192. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20200120-01. J Refract Surg. 2020. PMID: 32159823
-
Comparison of Capsular Tension Ring Implantation before vs. after Toric Intraocular Lens for Rotational Stability.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2024 Feb;241(2):186-191. doi: 10.1055/a-1964-7552. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2024. PMID: 36796415 Clinical Trial. English.
-
Can toric IOL rotation be minimized? Toric IOL-Capsular Tension Ring suturing technique and its clinical outcomes.Semin Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb 17;37(2):158-163. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1933545. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Semin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34096458
Cited by
-
Effect of capsule treatment on visual acuity and quality after phacoemulsification lens implantation in myopic patients with cataract.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jul 6;12(19):3882-3889. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3882. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38994309 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Technique of using Cionni-modified capsular tension ring in the management of severely traumatic lens subluxation.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul 18;16(7):1078-1083. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.07.12. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37465500 Free PMC article.
-
Propensity-matched comparison of postoperative stability and visual outcomes of toric intraocular lens with or without a capsular tension ring and updated meta-analysis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;261(4):989-998. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05851-y. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36201025
-
Capsular Tension Ring Implantation for Intraocular Lens Position: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025 Aug 1;143(8):643-651. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2025.1623. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40504499
-
Insights into the rotational stability of toric intraocular lens implantation: diagnostic approaches, influencing factors and intervention strategies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 13;11:1349496. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1349496. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38414624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kessel L, Andresen J, Tendal B, Erngaard D, Flesner P, Hjortdal J. Toric intraocular lenses in the correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2016;123(2):275–286. - PubMed
-
- Viestenz A, Walter S, Viestenz A, Behrens-Baumann W, Langenbucher A. Toric intraocular lenses and correction of astigmatism. Ophthalmologe. 2007;104(7):620–627. - PubMed
-
- Shah GD, Praveen MR, Vasavada AR, Vasavada VA, Rampal G, Shastry LR. Rotational stability of a toric intraocular lens: Influence of axial length and alignment in the capsular bag. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38(1):54–59. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Li J, Yang K, Li X, Zhu S. Combined special capsular tension ring and toric IOL implantation for management of astigmatism and high axial myopia with cataracts. Semin Ophthalmol. 2018;33(3):389–394. - PubMed
-
- Lee BS, Lindstrom RL, Reeves SW, Hardten DR. Modern management of astigmatism. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2013;53(1):65–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources