Auricular cartilage versus donor sclera as a wrapping of hydroxyapatite orbital implants
- PMID: 33747822
- PMCID: PMC7930529
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2021.03.17
Auricular cartilage versus donor sclera as a wrapping of hydroxyapatite orbital implants
Abstract
Aim: To retrospectively compare postoperative outcomes after primary enucleation and placement of a hydroxyapatite (HA) implant without wrapping, wrapped with auricular cartilage or donor sclera.
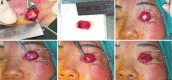
Methods: Medical records of patients presented as intraocular tumor or severe ocular injury were identified from the electronic medical record system. Cases underwent enucleation and HA orbital implantation were enrolled in this study and were divided into 3 groups according to the wrapping material of HA implant. Cases with autogenous cartilage caps were enrolled in group A (n=11), with donor sclera caps in group B (n=12), and without any wrapping material in group C (n=9). Follow-ups were set at 1, 2wk, 1, 3, 6, and 12mo after surgery.
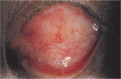
Results: Altogether 32 cases finished the follow-up and were enrolled in this study. Three cases (27.27%) in group A, 4 cases (33.33%) in group B, and 4 cases (44.44%) in group C developed one complication each after surgery. In group A, no HA exposure occurred, but conjunctival inclusion cyst occurred in one and severe conjunctive chemosis in two cases. In group B, one HA exposure occurred, conjunctive inclusion cysts occurred in one, severe conjunctive chemosis occurred in one, and conjunctival granuloma occurred in one case. In group C, one HA exposure occurred, severe conjunctive chemosis occurred in two cases, and conjunctival granuloma occurred in one case. The case of exposure of none-wrapped implant was noted in the first 6mo after placement of the orbital implant. The case of exposure of donor sclera-wrapped implant was noted at the 12mo after placement of the orbital implant. Both exposure cases were treated successfully with conservative treatment.
Conclusion: With low incidence of implant exposure and mild complications, auricular cartilage can be a good choice of alternative wrapping material of orbit implant with satisfied outcome.
Keywords: auricular cartilage; complication; donor sclera; hydroxyapatite orbital implants; wrapping.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bovine pericardium versus homologous sclera as a wrapping for hydroxyapatite orbital implants.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 May;19(3):189-93. doi: 10.1097/01.iop.0000062850.71572.7d. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12918552
-
Porous orbital implants, wraps, and PEG placement in the pediatric population after enucleation.Am J Ophthalmol. 2007 Jul;144(1):109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2007.03.042. Epub 2007 May 11. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17499206
-
The use of vicryl mesh in 200 porous orbital implants: a technique with few exposures.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003 Jan;19(1):53-61. doi: 10.1097/00002341-200301000-00007. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12544793
-
Complications of hydroxyapatite orbital implants. A review of 100 consecutive cases and a comparison of Dexon mesh (polyglycolic acid) with scleral wrapping.Ophthalmology. 1997 Feb;104(2):324-9. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30316-9. Ophthalmology. 1997. PMID: 9052640 Review.
-
Orbital implants in retinoblastoma patients: 23 years of experience and a review of the literature.Acta Ophthalmol. 2016 Mar;94(2):165-74. doi: 10.1111/aos.12915. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26603132 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison between local-made and imported porous polyethylene orbital implant: a randomized controlled equivalence trial and multicenter study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 18;17(10):1857-1863. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.10.12. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39430012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tabatabaee Z, Mazloumi M, Rajabi MT, Khalilzadeh O, Kassaee A, Moghimi S, Eftekhar H, Goldberg RA. Comparison of the exposure rate of wrapped hydroxyapatite (bio-eye) versus unwrapped porous polyethylene (medpor) orbital implants in enucleated patients. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;27(2):114–118. - PubMed
-
- Ye J, Gao Q, He JJ, Gao T, Ning QY, Xie JJ. Exposure rate of unwrapped hydroxyapatite orbital implants in enucleation surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016;100(6):860–865. - PubMed
-
- Custer PL. Enucleation: past, present, and future. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;16(5):316–321. - PubMed
-
- Rernulla HD, Rubin PAD, Shore JW, Sutula FC, Toaunsend DJ, Woog JJ, Jahrling KV. Complications of porous spherical orbital implants. Ophthalmology. 1995;102(4):586–593. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
