Formulation and Applications of Lipid-Based Nanovehicles: Spotlight on Self-emulsifying Systems
- PMID: 33747852
- PMCID: PMC7961215
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2021.006
Formulation and Applications of Lipid-Based Nanovehicles: Spotlight on Self-emulsifying Systems
Abstract
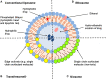
The drug delivery investigation field is continuously widened and adapted to overcome many factors such as poor drug solubility, absorption, rapid metabolism, the variability of drug plasma levels, cellular efflux and many others. Due to resemblance to body constituents and their biocompatibility, lipids offer a promising scheme for poorly water-soluble and lipophilic drugs. Various nanoparticles including vesicular systems, lipid particulate systems, and emulsion systems provide some unique benefits as pharmaceutical carriers in drug and biomolecules delivery systems. Nowadays synthesis is directed toward simple, costless techniques, therefore, self-emulsifying systems have gained superiority over the other carriers. Self nano-emulsifying systems composed of oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant emulsified upon contact with an aqueous medium, has been widely exploited. This review attempts to provide a comprehensive interpretation of different types of lipid-based carriers emphasizing on the self-nanoemulsifying system, why it is gaining interest, formulation, composition, and applications.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Lipids; Self-nanoemulsifying system; Solubility.
© 2021 The Authors.
References
-
- Mehanna M, Motawaa A, Samaha M. Pharmaceutical particulate carriers: lipid-based carriers. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;2(1):10–22.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources