Identification of an Individualized Immune-Related Prognostic Risk Score in Lung Squamous Cell Cancer
- PMID: 33747902
- PMCID: PMC7966508
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.546455
Identification of an Individualized Immune-Related Prognostic Risk Score in Lung Squamous Cell Cancer
Abstract
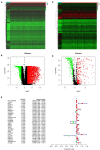
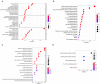
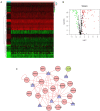
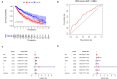
Background: Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is one of the most common histological subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and its morbidity and mortality are steadily increasing. The purpose of this study was to study the relationship between the immune-related gene (IRGs) profile and the outcome of LUSC in patients by analyzing datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Methods: We obtained publicly available LUSC RNA expression data and clinical survival data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), and filtered IRGs based on The ImmPort database. Then, we identified risk immune-related genes (r-IRGs) for model construction using Cox regression analysis and defined the risk score in this model as the immune gene risk index (IRI). Multivariate analysis was used to verify the independent prognostic value of IRI and its association with other clinicopathological features. Pearson correlation analysis was used to explore the molecular mechanism affecting the expression of IRGs and the correlation between IRI and immune cell infiltration. Results: We screened 15 r-IRGs for constructing the risk model. The median value of IRI stratified the patients and there were significant survival differences between the two groups (p = 4.271E-06). IRI was confirmed to be an independent prognostic factor (p < 0.001) and had a close correlation with the patients' age (p < 0.05). Interestingly, the infiltration of neutrophils or dendritic cells was strongly upregulated in the high-IRI groups (p < 0.05). Furthermore, by investigating differential transcription factors (TFs) and functional enrichment analysis, we explored potential mechanisms that may affect IRGs expression in tumor cells. Conclusion: In short, this study used 15 IRGs to build an effective risk prediction model, and demonstrated the significance of IRGs-based personalized immune scores in LUSC prognosis.
Keywords: TCGA; immune-related genes; lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC); prognosis; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2021 Zhuang, Li, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

