The Discovery of Novel BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Using a Pharmacophore Modeling and Virtual Screening Approach
- PMID: 33748144
- PMCID: PMC7969810
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.649434
The Discovery of Novel BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Using a Pharmacophore Modeling and Virtual Screening Approach
Abstract
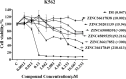
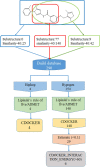
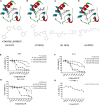
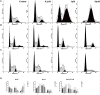
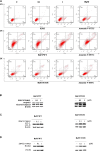
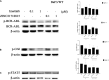
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) typically results from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 to produce the bcr-abl oncogene that when translated, yields the p210 BCR-ABL protein in more than 90% of all CML patients. This protein has constitutive tyrosine kinase activity that activates numerous downstream pathways that ultimately produces uncontrolled myeloid proliferation. Although the use of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, bosutinib, and ponatinib have increased the overall survival of CML patients, their use is limited by drug resistance and severe adverse effects. Therefore, there is the need to develop novel compounds that can overcome these problems that limit the use of these drugs. Therefore, in this study, we sought to find novel compounds using Hypogen and Hiphip pharmacophore models based on the structures of clinically approved BCR-ABL TKIs. We also used optimal pharmacophore models such as three-dimensional queries to screen the ZINC database to search for potential BCR-ABL inhibitors. The hit compounds were further screened using Lipinski's rule of five, ADMET and molecular docking, and the efficacy of the hit compounds was evaluated. Our in vitro results indicated that compound ZINC21710815 significantly inhibited the proliferation of K562, BaF3/WT, and BaF3/T315I leukemia cells by inducing cell cycle arrest. The compound ZINC21710815 decreased the expression of p-BCR-ABL, STAT5, and Crkl and produced apoptosis and autophagy. Our results suggest that ZINC21710815 may be a potential BCR-ABL inhibitor that should undergo in vivo evaluation.
Keywords: BCR-ABL; CML; ZINC21710815; apoptosis; autophagy; pharmacophore model.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Wang, Qiang, Zhao, Wu, Ashby, Li and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

