Divergently Transcribed ncRNAs in Escherichia coli: Refinement of the Transcription Starts Assumes Functional Diversification
- PMID: 33748186
- PMCID: PMC7967276
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.610453
Divergently Transcribed ncRNAs in Escherichia coli: Refinement of the Transcription Starts Assumes Functional Diversification
Abstract
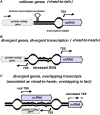
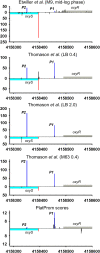
Non-coding regulatory RNAs (ncRNAs) comprise specialized group of essential genetically encoded biological molecules involved in the wide variety of cellular metabolic processes. The progressive increase in the number of newly identified ncRNAs and the defining of their genome location indicate their predominant nesting in intergenic regions and expression under the control of their own regulatory elements. At the same time, the regulation of ncRNA's transcription cannot be considered in isolation from the processes occurring in the immediate genetic environment. A number of experimental data indicate the notable impact of positional regulation of gene expression mediated by dynamic temporal DNA rearrangements accompanying transcription events in the vicinity of neighboring genes. This issue can be perceived as particularly significant for divergently transcribed ncRNAs being actually subjected to double regulatory pressure. Based on available results of RNAseq experiments for Escherichia coli, we screened out divergent ncRNAs and the adjacent genes for the exact positions of transcription start sites (TSSs) and relative efficiency of RNA production. This analysis revealed extension or shortening of some previously annotated ncRNAs resulting in modified secondary structure, confirmed stable expression of four ncRNAs annotated earlier as putative, and approved the possibility of expression of divergently transcribed ncRNAs containing repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP) elements. The biogenesis of secreted ncRNAs from divergently transcribed ffs, chiX, ralA, and ryhB is discussed taking into account positions of TSSs. Refinement of TSSs for the neighboring genes renders some ncRNAs as true antisense overlapping with 5'UTR of divergently transcribed mRNAs.
Keywords: REP elements; divergent transcription; genome annotation; non-coding RNAs; secreted RNAs.
Copyright © 2021 Kiselev, Markelova and Masulis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differentiation of ncRNAs from small mRNAs in Escherichia coli O157:H7 EDL933 (EHEC) by combined RNAseq and RIBOseq - ryhB encodes the regulatory RNA RyhB and a peptide, RyhP.BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 28;18(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3586-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28245801 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Transcription Start Sites and Promoter Motifs of Phytoplasmas.DNA Cell Biol. 2017 Dec;36(12):1081-1092. doi: 10.1089/dna.2016.3616. Epub 2017 Oct 17. DNA Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 29039971
-
Detection of natural antisense non-coding RNAs transcribed from Ncam1 in mice tissues at several developmental stages.Biomed Rep. 2015 Sep;3(5):663-667. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.482. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biomed Rep. 2015. PMID: 26405542 Free PMC article.
-
Long antisense non-coding RNAs and the epigenetic regulation of gene expression.Biomol Concepts. 2013 Aug;4(4):411-5. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2013-0014. Biomol Concepts. 2013. PMID: 25436590 Review.
-
[Non-coding RNA - from useless to essential].Cas Lek Cesk. 2016 Winter;155(7):370-376. Cas Lek Cesk. 2016. PMID: 27990832 Review. Czech.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

