Palivizumab reimbursement criteria and neonatal RSV hospitalisation: a regional retrospective review
- PMID: 33748434
- PMCID: PMC7925248
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjpo-2020-000985
Palivizumab reimbursement criteria and neonatal RSV hospitalisation: a regional retrospective review
Abstract
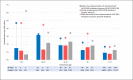
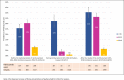
In Italy, reimbursement restrictions regarding palivizumab prophylaxis approved in 2016 have been revoked in 2017, restoring use in infants with Gestational Age (GA) >29 weeks. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) hospitalisations and prevalence of palivizumab use in infants aged <6 months during five seasons (2014-2019), were considered according to different GA. Although RSV hospitalisations rate showed no significant changes, during different seasons in all GA, lower prevalence of palivizumab use in 2016 (0.8% vs 0.3%), returned to a higher level following the revoke of restrictions. Changes in reimbursement criteria were not associated with neonatal RSV hospitalisations rate but with a significant impact on palivizumab use.
Keywords: neonatology; pharmacology; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases, American Academy of Pediatrics Bronchiolitis Guidelines Committee . Updated guidance for palivizumab prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatrics 2014;134:e620–38. 10.1542/peds.2014-1666 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
