DNA repair pathway activation features in follicular and papillary thyroid tumors, interrogated using 95 experimental RNA sequencing profiles
- PMID: 33748479
- PMCID: PMC7970325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06408
DNA repair pathway activation features in follicular and papillary thyroid tumors, interrogated using 95 experimental RNA sequencing profiles
Abstract
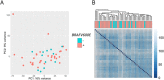
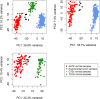
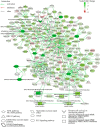
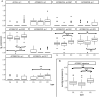
DNA repair can prevent mutations and cancer development, but it can also restore damaged tumor cells after chemo and radiation therapy. We performed RNA sequencing on 95 human pathological thyroid biosamples including 17 follicular adenomas, 23 follicular cancers, 3 medullar cancers, 51 papillary cancers and 1 poorly differentiated cancer. The gene expression profiles are annotated here with the clinical and histological diagnoses and, for papillary cancers, with BRAF gene V600E mutation status. DNA repair molecular pathway analysis showed strongly upregulated pathway activation levels for most of the differential pathways in the papillary cancer and moderately upregulated pattern in the follicular cancer, when compared to the follicular adenomas. This was observed for the BRCA1, ATM, p53, excision repair, and mismatch repair pathways. This finding was validated using independent thyroid tumor expression dataset PRJEB11591. We also analyzed gene expression patterns linked with the radioiodine resistant thyroid tumors (n = 13) and identified 871 differential genes that according to Gene Ontology analysis formed two functional groups: (i) response to topologically incorrect protein and (ii) aldo-keto reductase (NADP) activity. We also found RNA sequencing reads for two hybrid transcripts: one in-frame fusion for well-known NCOA4-RET translocation, and another frameshift fusion of ALK oncogene with a new partner ARHGAP12. The latter could probably support increased expression of truncated ALK downstream from 4th exon out of 28. Both fusions were found in papillary thyroid cancers of follicular histologic subtype with node metastases, one of them (NCOA4-RET) for the radioactive iodine resistant tumor. The differences in DNA repair activation patterns may help to improve therapy of different thyroid cancer types under investigation and the data communicated may serve for finding additional markers of radioiodine resistance.
Keywords: DNA repair; Follicular thyroid adenoma; Molecular biomarkers; Molecular pathway analysis; Papillary thyroid cancer; Personalized medicine; RNA sequencing; Radiation iodine therapy resistance; Systems biology; Thyroid cancer.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
















Similar articles
-
RET, NTRK, ALK, BRAF, and MET Fusions in a Large Cohort of Pediatric Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas.Thyroid. 2020 Dec;30(12):1771-1780. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0802. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Thyroid. 2020. PMID: 32495721
-
Classification of Thyroid Tumors Based on DNA Methylation Patterns.Thyroid. 2023 Sep;33(9):1090-1099. doi: 10.1089/thy.2023.0074. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Thyroid. 2023. PMID: 37392021
-
Follicular histotypes of oncocytic thyroid carcinomas do not carry mutations of the BRAF hot-spot.World J Surg. 2008 May;32(5):722-8. doi: 10.1007/s00268-007-9431-6. World J Surg. 2008. PMID: 18235983
-
Clinical utility of EZH1 mutations in the diagnosis of follicular-patterned thyroid tumors.Hum Pathol. 2018 Nov;81:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 May 1. Hum Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29723601 Review.
-
[Genetic factors predisposing to the development of papillary thyroid cancer].Endokrynol Pol. 2005 May-Jun;56(3):339-45. Endokrynol Pol. 2005. PMID: 16350729 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
A novel prognostic model for papillary thyroid cancer based on epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes.Cancer Med. 2022 Dec;11(23):4703-4720. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4836. Epub 2022 May 24. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35608185 Free PMC article.
-
Clinically relevant fusion oncogenes: detection and practical implications.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022 Dec 26;14:17588359221144108. doi: 10.1177/17588359221144108. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36601633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing Data for FFPE Tumor Blocks Can Be Used for Robust Estimation of Tumor Mutation Burden in Individual Biosamples.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 28;11:732644. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.732644. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34650919 Free PMC article.
-
Experimentally Deduced Criteria for Detection of Clinically Relevant Fusion 3' Oncogenes from FFPE Bulk RNA Sequencing Data.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 2;10(8):1866. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081866. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009413 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00261 triggers DNA damage via the miR-23a-3p/CELF2 axis to mitigate the malignant characteristics of 131I-resistant papillary thyroid carcinoma cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Oct 30;40:101858. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101858. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39552712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- La Vecchia C., Malvezzi M., Bosetti C., Garavello W., Bertuccio P., Levi F., Negri E. Thyroid cancer mortality and incidence: a global overview. Int. J. Canc. 2015;136:2187–2195. - PubMed
-
- Cabanillas M.E., McFadden D.G., Durante C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2783–2795. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L., Smith B.D., Aizenberg R., Rosenzweig A.B., Fleshman J.M., Matrisian L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Canc. Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Asa S.L. The current histologic classification of thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019;48:1–22. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

