Melatonin protects the heart and pancreas by improving glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in T2DM-induced rats
- PMID: 33748504
- PMCID: PMC7970364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06474
Melatonin protects the heart and pancreas by improving glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in T2DM-induced rats
Abstract
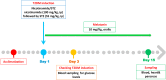
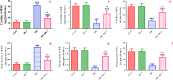
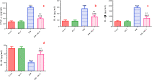
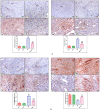
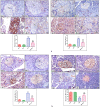
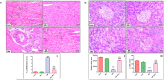
Cardiomyopathy and pancreatic injury are health issues associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and are characterized by elevated oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Melatonin (MLT) is a hormone with multifunctional antioxidant activity. The protective effects of MLT on the heart and pancreas during the early development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and pancreatic injury were investigated in male Wistar rats with T2DM. MLT (10 mg/kg) was administered daily by gavage for 15 days after diabetic induction. Treatment of diabetic rats with MLT significantly normalized the levels of serum glucose, HbA1-c, and the lipid profile and improved the insulin levels and insulin resistance compared with diabetic rats, affirming its antidiabetic effect. MLT significantly prevented the development of oxidative stress and sustained the levels of glutathione and glutathione peroxidase activity in the heart and pancreas of diabetic animals, indicating its antioxidant capacity. Additionally, MLT prevented the increase in proinflammatory cytokines and expression of Bax, caspase-3 and P53. Furthermore, MLT enhanced the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. MLT controlled the levels of troponin T and creatine kinase-MB and lactate dehydrogenase activity, indicating its anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects. Histological examinations confirmed the protective effects of MLT on T2DM-induced injury in the myocardium, pancreas and islets of Langerhans. In conclusion, the protective effects of melatonin on the heart and pancreas during the early development of T2DM are attributed to its antihyperglycemic, antilipidemic and antioxidant influences as well as its remarkable anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties.
Keywords: Heart; Hyperglycemia; Inflammatory cytokines; Melatonin; Oxidative stress; Pancreas.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Wild S.H., Walker J.J., Morling J.R., McAllister D.A., Colhoun H.M., Farran B., McGurnaghan S., McCrimmon R., Read S.H., Sattar N., Byrne C.D. Cardiovascular disease, cancer, and mortality among people with type 2 diabetes and alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease hospital admission. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:341–347. - PubMed
-
- Gurel-Gokmen B., Ipekci H., Oktay S., Alev B., Ustundag U.V., Ak E., Akakin D., Sener G., Emekli-Alturfan E., Yarat A., Tunali-Akbay T. Melatonin improves hyperglycemia induced damages in rat brain. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018;34 - PubMed
-
- Alonso N., Moliner P., Mauricio D. Springer New York LLC; 2018. Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and Treatment of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy; pp. 197–217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

