Automatic and Reliable Quantification of Tonic Dopamine Concentrations In Vivo Using a Novel Probabilistic Inference Method
- PMID: 33748573
- PMCID: PMC7970470
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05217
Automatic and Reliable Quantification of Tonic Dopamine Concentrations In Vivo Using a Novel Probabilistic Inference Method
Abstract
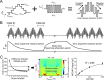
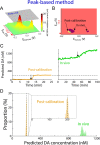
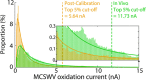
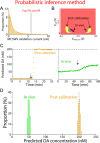
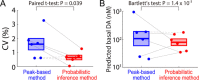
Dysregulation of the neurotransmitter dopamine (DA) is implicated in several neuropsychiatric conditions. Multiple-cyclic square-wave voltammetry (MCSWV) is a state-of-the-art technique for measuring tonic DA levels with high sensitivity (<5 nM), selectivity, and spatiotemporal resolution. Currently, however, analysis of MCSWV data requires manual, qualitative adjustments of analysis parameters, which can inadvertently introduce bias. Here, we demonstrate the development of a computational technique using a statistical model for standardized, unbiased analysis of experimental MCSWV data for unbiased quantification of tonic DA. The oxidation current in the MCSWV signal was predicted to follow a lognormal distribution. The DA-related oxidation signal was inferred to be present in the top 5% of this analytical distribution and was used to predict a tonic DA level. The performance of this technique was compared against the previously used peak-based method on paired in vivo and post-calibration in vitro datasets. Analytical inference of DA signals derived from the predicted statistical model enabled high-fidelity conversion of the in vivo current signal to a concentration value via in vitro post-calibration. As a result, this technique demonstrated reliable and improved estimation of tonic DA levels in vivo compared to the conventional manual post-processing technique using the peak current signals. These results show that probabilistic inference-based voltammetry signal processing techniques can standardize the determination of tonic DA concentrations, enabling progress toward the development of MCSWV as a robust research and clinical tool.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Caron M.; Beaulieu M.; Raymond V.; Gagne B.; Drouin J.; Lefkowitz R.; Labrie F. Dopaminergic receptors in the anterior pituitary gland. Correlation of [3H] dihydroergocryptine binding with the dopaminergic control of prolactin release. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2244–2253. 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)38065-1. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

