Highly Active Cellulose-Supported Poly(hydroxamic acid)-Cu(II) Complex for Ullmann Etherification
- PMID: 33748590
- PMCID: PMC7970499
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05840
Highly Active Cellulose-Supported Poly(hydroxamic acid)-Cu(II) Complex for Ullmann Etherification
Abstract
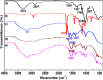
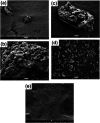
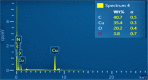
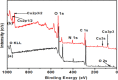
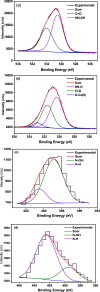
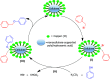
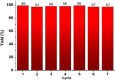
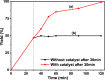
Highly active natural pandanus-extracted cellulose-supported poly(hydroxamic acid)-Cu(II) complex 4 was synthesized. The surface of pandanus cellulose was modified through graft copolymerization using purified methyl acrylate as a monomer. Then, copolymer methyl acrylate was converted into a bidentate chelating ligand poly(hydroxamic acid) via a Loosen rearrangement in the presence of an aqueous solution of hydroxylamine. Finally, copper species were incorporated into poly(hydroxamic acid) via the adsorption process. Cu(II) complex 4 was fully characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses. The cellulose-supported Cu(II) complex 4 was successfully applied (0.005 mol %) to the Ullmann etherification of aryl, benzyl halides, and phenacyl bromide with a number of aromatic phenols to provide the corresponding ethers with excellent yield [benzyl halide (70-99%); aryl halide (20-90%)]. Cu(II) complex 4 showed high stability and was easily recovered from the reaction mixture. It could be reused up to seven times without loss of its original catalytic activity. Therefore, Cu(II) complex 4 can be commercially utilized for the preparation of various ethers, and this synthetic technique could be a part in the synthesis of natural products and medicinal compounds.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Puthiaraj P.; Ahn W.-S. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles supported on a microporous covalent triazine polymer: an efficient and reusable catalyst for O-arylation reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1701–1709. 10.1039/C5CY01590A. - DOI
-
- Beletskaya I. P.; Cheprakov A. V. Copper in cross-coupling reactions: The post-Ullmann chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2337–2364. 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.014. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

