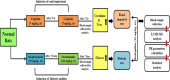
Effect of Disease State on the Pharmacokinetics of Bedaquiline in Renal-Impaired and Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 33748607
- PMCID: PMC7970569
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06165
Effect of Disease State on the Pharmacokinetics of Bedaquiline in Renal-Impaired and Diabetic Rats
Abstract
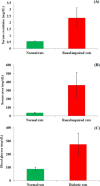
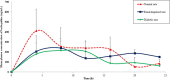
Bedaquiline (TMC-207) is a key anti-tubercular drug to fight against multidrug resistance tuberculosis. Little information is available till date on the impact of any disease state toward its pharmacokinetic behavior. The present research work aimed to investigate the effect of renal impairment and diabetes mellitus on the oral pharmacokinetics of bedaquiline in the rat model. Renal impairment and diabetes mellitus were induced in the Wistar rat model separately using cisplatin and streptozotocin, respectively, and thereafter, an oral pharmacokinetic study of bedaquiline was carried out in the individual disease models as well as in the normal rat model. Pharmacokinetic parameters of bedaquiline were not altered markedly in cisplatin-induced renal-impaired rats compared to normal rats except an area under the curve (AUC) for plasma concentration of bedaquiline in the experimental time frame (AUC0-t ) reduced to 3477 ± 228 from 4984 ± 1174 ng h/mL, respectively. Maximum plasma concentrations of bedaquiline (259 ± 77 ng/mL), AUC0-t (3112 ± 1046 ng h/mL), and AUC0-∞ (3673 ± 1493 ng h/mL) were significantly reduced along with an increase in the clearance of bedaquiline (3.1 ± 1.1 L/h/kg) in the case of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats compared to respective pharmacokinetic parameters of bedaquiline (482 ± 170 ng/mL, 4984 ± 1174 ng h/mL, and 6137 ± 1542 ng h/mL) in the normal rats. Preclinical findings suggest that dose adjustment of bedaquiline is required in the diabetes mellitus condition to prevent the therapeutic failure of bedaquiline treatment, but clinical exploration is needed to establish the fact. It is the first report for the consequence of renal impairment and diabetes mellitus on the pharmacokinetics of bedaquiline in the preclinical model.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Magotra A.; Sharma A.; Singh S.; Ojha P. K.; Kumar S.; Bokolia N.; Wazir P.; Sharma S.; Khan I. A.; Singh P. P.; Vishwakarma R. A.; Singh G.; Nandi U. Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, efficacy and toxicity profiling of a potential nitrofuranyl methyl piperazine derivative IIIM-MCD-211 for oral tuberculosis therapy via in-silico–in-vitro–in-vivo approach. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 151–160. 10.1016/j.pupt.2017.11.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

