Role of biomaterials in the diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and study of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 33748672
- PMCID: PMC7962632
- DOI: 10.1007/s42247-021-00165-x
Role of biomaterials in the diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and study of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
Recently emerged novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the resulting corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) led to urgent search for methods to prevent and treat COVID-19. Among important disciplines that were mobilized is the biomaterials science and engineering. Biomaterials offer a range of possibilities to develop disease models, protective, diagnostic, therapeutic, monitoring measures, and vaccines. Among the most important contributions made so far from this field are tissue engineering, organoids, and organ-on-a-chip systems, which have been the important frontiers in developing tissue models for viral infection studies. Also, due to low bioavailability and limited circulation time of conventional antiviral drugs, controlled and targeted drug delivery could be applied alternatively. Fortunately, at the time of writing this paper, we have two successful vaccines and new at-home detection platforms. In this paper, we aim to review recent advances of biomaterial-based platforms for protection, diagnosis, vaccination, therapeutics, and monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 and discuss challenges and possible future research directions in this field.
Keywords: Biomaterials; COVID-19; Organ-on-a-chip; Organoid; SARS-2; Tissue engineering.
© Qatar University and Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
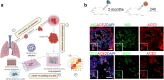
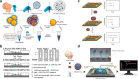
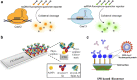
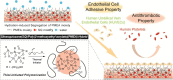
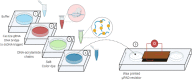
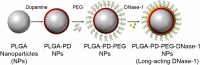
References
-
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. Jama. 2020;324(8):782–793. - PubMed
-
- H.T. Sun, AM, B.Q. Luu, J. Widdicombe, N. Ashammakhi, S. Li, Recent advances in in vitro lung microphysiological systems for Covid-19 modeling and drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. (2020)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
