The silent pandemic: Emergent antibiotic resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33748695
- PMCID: PMC7955580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102304
The silent pandemic: Emergent antibiotic resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
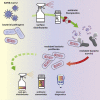
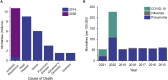
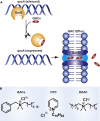
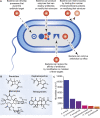
The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has highlighted the importance of the rapid development of vaccines and antivirals. However, the potential for the emergence of antibiotic resistances due to the increased use of antibacterial cleaning products and therapeutics presents an additional, underreported threat. Most antibacterial cleaners contain simple quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs); however, these compounds are steadily becoming less effective as antibacterial agents. QACs are extensively used in SARS-CoV-2-related sanitization in clinical and household settings. Similarly, due to the danger of secondary infections, antibiotic therapeutics are increasingly used as a component of COVID-19 treatment regimens, even in the absence of a bacterial infection diagnosis. The increased use of antibacterial agents as cleaners and therapeutics is anticipated to lead to novel resistances in the coming years.
Keywords: Applied Chemistry; Microbiology; Multi-Drug Resistant Organisms.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
W.M.W. has intellectual property covering novel quaternary ammonium compounds. A.L.F. is a member of the Editorial Advisory Board of iScience.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Use of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic and Beyond: Consideration of Environmental Implications.Environ Sci Technol Lett. 2020 Jun 26;7(9):622-631. doi: 10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00437. eCollection 2020 Sep 8. Environ Sci Technol Lett. 2020. PMID: 37566314 Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 variants and COVID-19 vaccines: Current challenges and future strategies.Int Rev Immunol. 2023;42(6):393-414. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2022.2079642. Epub 2022 May 28. Int Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 35635216 Review.
-
Resistance to phenicol compounds following adaptation to quaternary ammonium compounds in Escherichia coli.Vet Microbiol. 2012 Jul 6;158(1-2):147-52. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.030. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Vet Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22397929
-
Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by Commercially Available Disinfectants and Cleaners.Biocontrol Sci. 2022;27(4):223-228. doi: 10.4265/bio.27.223. Biocontrol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36567119
-
Emergence of resistance to antibacterial agents: the role of quaternary ammonium compounds--a critical review.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012 May;39(5):381-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.01.011. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012. PMID: 22421329 Review.
Cited by
-
Death at the interface: Nanotechnology's challenging frontier against microbial surface colonization.Front Chem. 2022 Oct 13;10:1003234. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1003234. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36311433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hospital Antibiotic Use during COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;12(1):168. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010168. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671369 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ceftazidime and Cefepime in the Management of COVID-19 Patients: Single Center Report from Egypt.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;10(11):1278. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111278. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827216 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiotics against antimicrobial resistance: harnessing the power of nanoscale materials and technologies.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 12;20(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01573-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35953826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quaternary Phosphonium Compounds: An Examination of Non-Nitrogenous Cationic Amphiphiles That Evade Disinfectant Resistance.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 11;8(2):387-397. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00611. Epub 2022 Jan 25. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35077149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ancillotti M., Eriksson S., Veldwijk J., Nihlén Fahlquist J., Andersson D.I., Godskesen T. Public awareness and individual responsibility needed for judicious use of antibiotics: a qualitative study of public beliefs and perceptions. BMC Public Health. 2018;18:1153. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6047-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC . CDC; 2020. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
-
- Blasco M.L., Buesa J., Colomina J., Forner M.J., Galindo M.J., Navarro J., Noceda J., Redón J., Signes-Costa J., Navarro D. Co-detection of respiratory pathogens in patients hospitalized with Coronavirus viral disease-2019 pneumonia. J. Med. Virol. 2020;92:1799–1801. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25922. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

