New threatening of SARS-CoV-2 coinfection and strategies to fight the current pandemic
- PMID: 33748740
- PMCID: PMC7963520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medidd.2021.100089
New threatening of SARS-CoV-2 coinfection and strategies to fight the current pandemic
Abstract
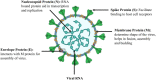
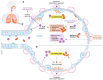
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a global pandemic. The COVID-19 outbreak caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has overloaded healthcare systems that need medication to be rapidly established, at least to minimize the incidence of COVID-19. The coinfection with other microorganisms has drastically affected human health. Due to the utmost necessity to treat the patient infected with COVID-19 earliest, poor diagnosis and misuse of antibiotics may lead the world where no more drugs are available even to treat mild infections. Besides, sanitizers and disinfectants used to help minimize widespread coronavirus infection risk also contribute to an increased risk of antimicrobial resistance. To ease the situation, zinc supplements' potentiality has been explored and found to be an effective element to boost the immune system. Zinc also prevents the entry of the virus by increasing the ciliary beat frequency. Furthermore, the limitations of current antiviral agents such as a narrow range and low bioavailability can be resolved using nanomaterials, which are considered an important therapeutic alternative for the next generation. Thus, the development of new antiviral nanoagents will significantly help tackle many potential challenges and knowledge gaps. This review paper provides profound insight into how COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are interrelated and the possible implications and current strategies to fight the ongoing pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; antimicrobial resistance; antiviral agents; immune system; nanomaterials.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance as a Hidden Menace Lurking Behind the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Global Impacts of Too Much Hygiene on AMR.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 15;11:590683. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.590683. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33384670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) during the COVID-19 pandemic.Anaerobe. 2022 Apr;74:102518. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2022.102518. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Anaerobe. 2022. PMID: 35063599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interrelationships between antimicrobial resistance, COVID-19, past, and future pandemics.J Infect Public Health. 2021 Jan;14(1):53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.10.018. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Infect Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33341485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repurposing Polyether Ionophores as a New-Class of Anti-SARS-Cov-2 Agents as Adjunct Therapy.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Jul 6;80(8):273. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03366-1. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37414909 Review.
-
Worldwide prevalence of microbial agents' coinfection among COVID-19 patients: A comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24151. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24151. Epub 2021 Dec 1. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34851526 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Current Challenges and Health Concern.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 15;12:693916. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.693916. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34211506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparedness for the Dengue Epidemic: Vaccine as a Viable Approach.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;10(11):1940. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111940. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coinfections and Superinfections Associated with COVID-19 in Colombia: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jul 20;59(7):1336. doi: 10.3390/medicina59071336. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37512147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
