Formulation development of itraconazole PEGylated nano-lipid carriers for pulmonary aspergillosis using hot-melt extrusion technology
- PMID: 33748741
- PMCID: PMC7973123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2021.100074
Formulation development of itraconazole PEGylated nano-lipid carriers for pulmonary aspergillosis using hot-melt extrusion technology
Abstract
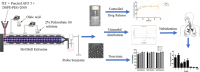
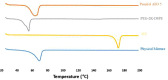
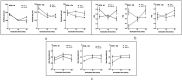
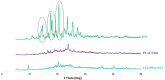
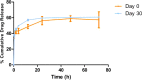
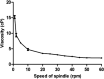
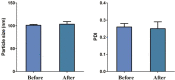
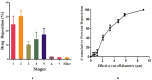
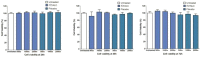
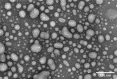
Pulmonary delivery is a promising alternative for the oral treatment of pulmonary aspergillosis. This study aimed to develop continuous and scalable itraconazole PEGylated nano-lipid carriers (ITZ-PEG-NLC) for inhalation delivery. The feasibility of preparing NLCs utilizing hot-melt extrusion (HME) coupled with probe sonication was investigated. The process parameters for HME and sonication were varied to optimize the formulation. ITZ-PEG-NLC (particle size, 101.20 ± 1.69 nm; polydispersity index, 0.26 ± 0.01) was successfully formulated. The drug entrapment efficiency of ITZ-PEG-NLC was 97.28 ± 0.50%. Transmission electron microscopy was used to characterize the shape of the particles. The developed formulations were evaluated for their aerodynamic properties for pulmonary delivery. The lung deposition of ITZ-PEG-NLC was determined using an Anderson Cascade Impactor and Philips Respironics Sami the Seal Nebulizer Compressor. In vitro cytotoxicity studies were performed using A549 cells. A burst-release pattern was observed in ITZ-PEG-NLC with a drug release of 41.74 ± 1.49% in 60 min. The in vitro aerosolization of the ITZ-PEG-NLC formulation showed a mass median aerodynamic diameter of 3.51 ± 0.28 μm and a geometric standard deviation of 2.44 ± 0.49. These findings indicate that HME technology could be used for the production of continuous scalable ITZ-PEG-NLC.
Keywords: Hot-melt extrusion; Inhalation; Itraconazole; Nanostructured lipid carriers; PEGylation; Pulmonary drug delivery.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Alvarez C.A., Wiederhold N.P., McConville J.T., Peters J.I., Najvar L.K., Graybill J.R., Coalson J.J., Talbert R.L., Burgess D.S., Bocanegra R., Johnston K.P., Williams R.O. Aerosolized nanostructured itraconazole as prophylaxis against invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Inf. Secur. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2007.01.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dailey L.A., Schmehl T., Gessler T., Wittmar M., Grimminger F., Seeger W., Kissel T. Nebulization of biodegradable nanoparticles: Impact of nebulizer technology and nanoparticle characteristics on aerosol features. J. Control. Release. 2003;86:131–144. doi: 10.1016/S0168-3659(02)00370-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

