Magnetic Microdevices for MRI-Based Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Viruses
- PMID: 33748768
- PMCID: PMC7978173
- DOI: 10.1109/ojemb.2020.3026234
Magnetic Microdevices for MRI-Based Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Viruses
Abstract
Goal: To develop a micron-scale device that can operate as an MRI-based reporter for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 virus.
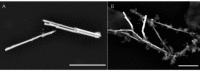
Methods: Iron rod microdevices were constructed via template-guided synthesis and suspended in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Heat-inactivated SARS-CoV-2 viruses were added to the samples and imaged with low-field MRI.
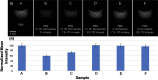
Results: MRI of microdevices and viruses showed decreased signal intensity at low concentrations of viruses that recovered at higher concentrations. Electron micrographs suggest that reduced MRI intensity may be due to concentration-dependent shielding of water protons from local magnetic inhomogeneities caused by the iron microdevices.
Conclusions: The preliminary results presented in this letter provide justification for further studies exploring the potential diagnostic role of magnetic microdevices in assessing the presence and concentration of SARS-CoV-2 viruses.
Keywords: COVID; MRI; coronavirus; magnetic microdevices; theranostic.
Figures
References
-
- Debbage P. and Jaschke W., “Molecular imaging with nanoparticles: Giant roles for dwarf actors,” Histochem. Cell Biol., vol. 130, no. 5, pp. 845–75, Nov. 2008. - PubMed
-
- Barclay R. et al. , “Nanotrap particles improve detection of SARS-CoV-2 for pooled sample methods, extraction-free saliva methods, and extraction-free transport medium methods,” bioRxiv, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.25.172510
-
- Perez J. M., Simeone F. J., Saeki Y., Josephson L., and Weissleder R., “Viral-induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles allows the detection of viral particles in biological media,” J. Amer. Chem. Soc., vol. 125, no. 34, pp. 10192–10193, Aug. 2003. - PubMed
-
- Haun J. B., Yoon T. J., Lee H., and Weissleder R., “Magnetic nanoparticle biosensors,” Wiley Interdisciplinary Rev.: Nanomedicine Nanobiotechnology, vol. 2, no. 3. pp. 291–304, May 2010. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

