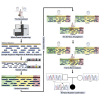
Analysis workflow to assess de novo genetic variants from human whole-exome sequencing
- PMID: 33748785
- PMCID: PMC7960548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100383
Analysis workflow to assess de novo genetic variants from human whole-exome sequencing
Abstract
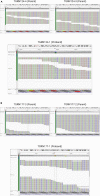
Here, we present a protocol to analyze de novo genetic variants derived from the whole-exome sequencing (WES) of proband-parent trios. We provide stepwise instructions for using existing pipelines to call de novo mutations (DNMs) and determine whether the observed number of such mutations is enriched relative to the expected number. This protocol may be extended to any human disease trio-based cohort. Cohort size is a limiting determinant to the discovery of high-confidence pathogenic DNMs. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Dong et al. (2020).
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Genetics; Genomics; High-throughput screening; Sequence analysis; Sequencing.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantifying concordant genetic effects of de novo mutations on multiple disorders.Elife. 2022 Jun 6;11:e75551. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75551. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35666111 Free PMC article.
-
A de novo pathogenic CSNK1E mutation identified by exome sequencing in family trios with epileptic encephalopathy.Hum Mutat. 2019 Mar;40(3):281-287. doi: 10.1002/humu.23690. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 30488659
-
Identification of De Novo DNMT3A Mutations That Cause West Syndrome by Using Whole-Exome Sequencing.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2483-2493. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0483-9. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28386848
-
Diagnosing rare diseases after the exome.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018 Dec 17;4(6):a003392. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a003392. Print 2018 Dec. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018. PMID: 30559314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of de novo germline mutations and causal genes for sporadic diseases using trio-based whole-exome/genome sequencing.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018 May;93(2):1014-1031. doi: 10.1111/brv.12383. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018. PMID: 29154454 Review.
Cited by
-
Familial and syndromic forms of arachnoid cyst implicate genetic factors in disease pathogenesis.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Mar 10;33(6):3012-3025. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac257. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 35851401 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical methods for assessing the effects of de novo variants on birth defects.Hum Genomics. 2024 Mar 14;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00590-z. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38486307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTEN mutations impair CSF dynamics and cortical networks by dysregulating periventricular neural progenitors.Nat Neurosci. 2025 Mar;28(3):536-557. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01865-3. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Nat Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39994410
-
A novel SMARCC1 BAFopathy implicates neural progenitor epigenetic dysregulation in human hydrocephalus.Brain. 2024 Apr 4;147(4):1553-1570. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad405. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38128548 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of key signaling regulators of cerebrovascular development in vein of Galen malformations.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 17;14(1):7452. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43062-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37978175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Homsy J., Zaidi S., Shen Y., Ware J.S., Samocha K.E., Karczewski K.J., DePalma S.R., McKean D., Wakimoto H., Gorham J. De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies. Science. 2015;350:1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9396. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous