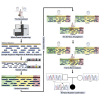
Analysis workflow to assess de novo genetic variants from human whole-exome sequencing
- PMID: 33748785
- PMCID: PMC7960548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100383
Analysis workflow to assess de novo genetic variants from human whole-exome sequencing
Abstract
Here, we present a protocol to analyze de novo genetic variants derived from the whole-exome sequencing (WES) of proband-parent trios. We provide stepwise instructions for using existing pipelines to call de novo mutations (DNMs) and determine whether the observed number of such mutations is enriched relative to the expected number. This protocol may be extended to any human disease trio-based cohort. Cohort size is a limiting determinant to the discovery of high-confidence pathogenic DNMs. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Dong et al. (2020).
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Genetics; Genomics; High-throughput screening; Sequence analysis; Sequencing.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Homsy J., Zaidi S., Shen Y., Ware J.S., Samocha K.E., Karczewski K.J., DePalma S.R., McKean D., Wakimoto H., Gorham J. De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies. Science. 2015;350:1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9396. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous