Nanotechnology advances in pathogen- and host-targeted antiviral delivery: multipronged therapeutic intervention for pandemic control
- PMID: 33748879
- PMCID: PMC7982277
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-021-00965-y
Nanotechnology advances in pathogen- and host-targeted antiviral delivery: multipronged therapeutic intervention for pandemic control
Abstract
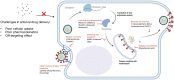
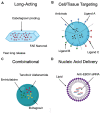
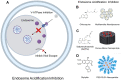
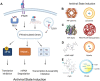
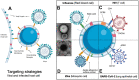
The COVID-19 pandemic's high mortality rate and severe socioeconomic impact serve as a reminder of the urgent need for effective countermeasures against viral pandemic threats. In particular, effective antiviral therapeutics capable of stopping infections in its tracks is critical to reducing infection fatality rate and healthcare burden. With the field of drug delivery witnessing tremendous advancement in the last two decades owing to a panoply of nanotechnology advances, the present review summarizes and expounds on the research and development of therapeutic nanoformulations against various infectious viral pathogens, including HIV, influenza, and coronaviruses. Specifically, nanotechnology advances towards improving pathogen- and host-targeted antiviral drug delivery are reviewed, and the prospect of achieving effective viral eradication, broad-spectrum antiviral effect, and resisting viral mutations are discussed. As several COVID-19 antiviral clinical trials are met with lackluster treatment efficacy, nanocarrier strategies aimed at improving drug pharmacokinetics, biodistributions, and synergism are expected to not only contribute to the current disease treatment efforts but also expand the antiviral arsenal against other emerging viral diseases.
Keywords: Antiviral state; Antivirals; COVID-19; Drug delivery; Host-targeted antiviral; Nanodecoy; Nanoparticles; Nanosponge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human respiratory viral infections: Current status and future prospects of nanotechnology-based approaches for prophylaxis and treatment.Life Sci. 2021 Aug 1;278:119561. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119561. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33915132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancement in Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System Against Viral Infections.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Jan 14;22(1):47. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01908-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 33447909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in vaccine delivery systems against viral infectious diseases.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Aug;11(4):1401-1419. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00945-2. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33694083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticulate delivery systems for antiviral drugs.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010;21(2):53-70. doi: 10.3851/IMP1684. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010. PMID: 21107015 Review.
-
Nanotheranostics against COVID-19: From multivalent to immune-targeted materials.J Control Release. 2020 Dec 10;328:112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.060. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32882269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrocyclic peptides as a new class of targeted protein degraders.RSC Chem Biol. 2025 Jan 15;6(3):326-337. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00199k. eCollection 2025 Mar 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 39822773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinson's Disease and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Particularities of Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Regarding Pathogenesis and Treatment.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 26;10(5):1000. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051000. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanosponges: An overlooked promising strategy to combat SARS-CoV-2.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Oct;27(10):103330. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.07.015. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 35908684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 Mar;21(3):181-200. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00371-6. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35042991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary drug delivery: an effective and convenient delivery route to combat COVID-19.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Mar;13(3):705-715. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01251-1. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36260223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taxonomic. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). 2020. https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy/
-
- Bryan-Marrugo OL, Ramos-Jiménez J, Barrera-Saldaña H, Rojas-Martínez A, Vidaltamayo R, Rivas-Estilla AM. History and progress of antiviral drugs: from acyclovir to direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) for Hepatitis C. Medicina Universitaria. 2015;17(68):165–174. doi: 10.1016/j.rmu.2015.05.003. - DOI
-
- Rodriguez Mega E. COVID has killed more than one million people. How many more will die? Nature. 2020. 10.1038/d41586-020-02762-y. - PubMed
-
- Organization WH. “Solidarity” clinical trial for COVID-19 treatments. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

