Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Early Detect Tissue Injury and Microcirculation Alteration in Hepatic Injury Induced by Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion in a Rat Model
- PMID: 33749079
- PMCID: PMC8451931
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.27604
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Early Detect Tissue Injury and Microcirculation Alteration in Hepatic Injury Induced by Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion in a Rat Model
Abstract
Background: Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) can provide quantitative information about water diffusion and perfusion that can be used to evaluate hepatic injury, but it has not been studied in hepatic injury induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion (IIR). Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide perfusion data, but it is unclear whether it can provide useful information for assessing hepatic injury induced by IIR.
Purpose: To examine whether IVIM and DCE-MRI can detect early IIR-induced hepatic changes, and to evaluate the relationship between IVIM and DCE-derived parameters and biochemical indicators and histological scores.
Study type: Prospective pre-clinical study.
Population: Forty-two male Sprague-Dawley rats.
Field strength/sequence: IVIM-diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) using diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging sequence and DCE-MRI using fast spoiled gradient recalled-based sequence at 3.0 T.
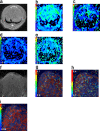
Assessment: All rats were randomly divided into the control group (Sham), the simple ischemia group, the ischemia-reperfusion (IR) group (IR1h, IR2h, IR3h, and IR4h) in a model of secondary hepatic injury caused by IIR, and IIR was induced by clamping the superior mesenteric artery for 60 minutes and then removing the vascular clamp. Advanced Workstation (AW) 4.6 was used to calculate the imaging parameters (apparent diffusion coefficient [ADC], true diffusion coefficient [D], perfusion-related diffusion [D* ] and volume fraction [f]) of IVIM. OmniKinetics (OK) software was used to calculate the DCE imaging parameters (Ktrans , Kep , and Ve ). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were analyzed with an automatic biochemical analyzer. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was assessed using the nitro-blue tetrazolium method. Malondialdehyde (MDA) was determined by thiobarbituric acid colorimetry. Histopathology was performed with hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Statistical tests: One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni post-hoc tests were used to analyze the imaging parameters and biochemical indicators among the different groups. Pearson correlation analysis was applied to determine the correlation between imaging parameters and biochemical indicators or histological score.
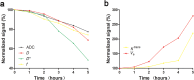
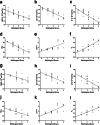
Results: ALT and MDA reached peak levels at IR4h, while SOD reached the minimum level at IR4h (all P < 0.05). ADC, D, D* , and f gradually decreased as reperfusion continued, and Ktrans and Ve gradually increased (all P < 0.05). The degrees of change for f and Ve were greater than those of other imaging parameters at IR1h (all P < 0.05). All groups showed good correlation between imaging parameters and SOD and MDA (r[ADC] = 0.615, -0.666, r[D] = 0.493, -0.612, r[D* ] = 0.607, -0.647, r[f] = 0.637, -0.682, r[Ktrans ] = -0.522, 0.500, r[Ve ] = -0.590, 0.665, respectively; all P < 0.05). However, the IR groups showed poor or no correlation between the imaging parameters and SOD and MDA (P [Ktrans and MDA] = 0.050, P [D and SOD] = 0.125, P [the remaining imaging parameters] < 0.05). All groups showed a positive correlation between histological score and Ktrans and Ve (r = 0.775, 0.874, all P < 0.05), and a negative correlation between histological score and ADC, D, f, and D* (r = -0.739, -0.821, -0.868, -0.841, respectively; all P < 0.05). For the IR groups, there was a positive correlation between histological score and Ktrans and Ve (r = 0.747, 0.802, all P < 0.05), and a negative correlation between histological score and ADC, D, f, and D* (r = -0.567, -0.712, -0.715, -0.779, respectively; all P < 0.05).
Data conclusion: The combined application of IVIM and DCE-MRI has the potential to be used as an imaging tool for monitoring IIR-induced hepatic histopathology.
Level of evidence: 1 TECHNICAL EFFICACY STAGE: 2.
Keywords: dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI; intestinal ischemia-reperfusion; intravoxel incoherent motion; secondary hepatic injury.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Zhao W, Gan X, Su G, et al. The interaction between oxidative stress and mast cell activation plays a role in acute lung injuries induced by intestinal ischemia‐reperfusion. J Surg Res 2014;187:542‐552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

