Development of an NMR-Based Platform for the Direct Structural Annotation of Complex Natural Products Mixtures
- PMID: 33750122
- PMCID: PMC8330833
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01076
Development of an NMR-Based Platform for the Direct Structural Annotation of Complex Natural Products Mixtures
Abstract
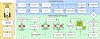
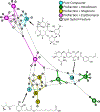
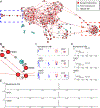
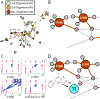
The development of new "omics" platforms is having a significant impact on the landscape of natural products discovery. However, despite the advantages that such platforms bring to the field, there remains no straightforward method for characterizing the chemical landscape of natural products libraries using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (2D-NMR) experiments. NMR analysis provides a powerful complement to mass spectrometric approaches, given the universal coverage of NMR experiments. However, the high degree of signal overlap, particularly in one-dimensional NMR spectra, has limited applications of this approach. To address this issue, we have developed a new data analysis platform for complex mixture analysis, termed MADByTE (Metabolomics and Dereplication by Two-Dimensional Experiments). This platform employs a combination of TOCSY and HSQC spectra to identify spin system features within complex mixtures and then matches spin system features between samples to create a chemical similarity network for a given sample set. In this report we describe the design and construction of the MADByTE platform and demonstrate the application of chemical similarity networks for both the dereplication of known compound scaffolds and the prioritization of bioactive metabolites from a bacterial prefractionated extract library.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Hubert J; Nuzillard JM; Renault JH Phytochem. Rev 2017, 16 (1), 55–95.
-
- Wang M; Carver JJ; Phelan VV; Sanchez LM; Garg N; Peng Y; Nguyen DD; Watrous J; Kapono CA; Luzzatto-Knaan T; Porto C; Bouslimani A; Melnik AV; Meehan MJ; Liu WT; Crüsemann M; Boudreau PD; Esquenazi E; Sandoval-Calderón M; Kersten RD; Pace LA; Quinn RA; Duncan KR; Hsu CC; Floros DJ; Gavilan RG; Kleigrewe K; Northen T; Dutton RJ; Parrot D; Carlson EE; Aigle B; Michelsen CF; Jelsbak L; Sohlenkamp C; Pevzner P; Edlund A; McLean J; Piel J; Murphy BT; Gerwick L; Liaw CC; Yang YL; Humpf HU; Maansson M; Keyzers RA; Sims AC; Johnson AR; Sidebottom AM; Sedio BE; Klitgaard A; Larson CB; Boya CAP; Torres-Mendoza D; Gonzalez DJ; Silva DB; Marques LM; Demarque DP; Pociute E; O’Neill EC; Briand E; Helfrich EJN; Granatosky EA; Glukhov E; Ryffel F; Houson H; Mohimani H; Kharbush JJ; Zeng Y; Vorholt JA; Kurita KL; Charusanti P; McPhail KL; Nielsen KF; Vuong L; Elfeki M; Traxler MF; Engene N; Koyama N; Vining OB; Baric R; Silva RR; Mascuch SJ; Tomasi S; Jenkins S; Macherla V; Hoffman T; Agarwal V; Williams PG; Dai J; Neupane R; Gurr J; Rodríguez AMC; Lamsa A; Zhang C; Dorrestein K; Duggan BM; Almaliti J; Allard PM; Phapale P; Nothias LF; Alexandrov T; Litaudon M; Wolfender JL; Kyle JE; Metz TO; Peryea T; Nguyen DT; VanLeer D; Shinn P; Jadhav A; Müller R; Waters KM; Shi W; Liu X; Zhang L; Knight R; Jensen PR; Palsson B; Pogliano K; Linington RG; Gutiérrez M; Lopes NP; Gerwick WH; Moore BS; Dorrestein PC; Bandeira N Nat. Biotechnol 2016, 34 (8), 828–837. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Annesley TM Clin. Chem 2003, 49 (7), 1041–1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

