Effects of X Chromosome Monosomy and Genomic Imprinting on Observational Markers of Social Anxiety in Prepubertal Girls with Turner Syndrome
- PMID: 33751331
- PMCID: PMC9662592
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-021-04896-y
Effects of X Chromosome Monosomy and Genomic Imprinting on Observational Markers of Social Anxiety in Prepubertal Girls with Turner Syndrome
Abstract
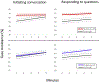
Previous studies have suggested that girls with Turner syndrome (TS) exhibit symptoms of social anxiety during interactions with others. However, few studies have quantified these behaviors during naturalistic face-to-face social encounters. In this study, we coded observational markers of social anxiety in prepubertal girls with TS and age-matched controls during a 10-min social encounter with an unfamiliar examiner. Results showed that girls with TS exhibited significantly higher levels of gaze avoidance compared to controls. Impairments in social gaze were particularly increased in girls with a maternally retained X chromosome (Xm), suggesting a genomic imprinting effect. These data indicate that social gaze avoidance may be a critical behavioral marker for identifying early social dysfunction in young girls with TS.
Keywords: Behavioral observations; Gaze avoidance; Genomic imprinting; Turner syndrome.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
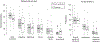
References
-
- Bakeman R, & Quera V (1995). Analyzing interaction: Sequential analysis with SDIS and GSEQ. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Bakeman R, & Quera V (2011). Sequential Analysis and Observational Methods for the Behavioral Sciences. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Bishop DVM, Canning E, Elgar K, Morris E, Jacobs PA, & Skuse DH (2000). Distinctive patterns of memory function in subgroups of females with Turner syndrome: Evidence for imprinted loci on the X-chromosome affecting neurodevelopment. Neuropsychologia, 38(5), 712–721. 10.1016/S0028-3932(99)00118-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bondy CA, Hougen HY, Zhou J, & Cheng CM (2012). Genomic imprinting and Turner syndrome. Pediatric Endocrinology Review, 9(2), 728–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

