Storm of Cardiovascular Markers After LPS Administration in Human Volunteers
- PMID: 33751402
- PMCID: PMC7983963
- DOI: 10.1007/s12265-021-10109-9
Storm of Cardiovascular Markers After LPS Administration in Human Volunteers
Abstract
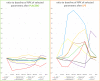
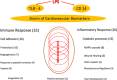
Acute infections are associated with an elevated cardiovascular risk. However, little is known about the interactions of acute inflammatory responses and the cardiovascular system. We therefore aimed to evaluate effects of acute inflammatory stimuli mediated by LPS administration on a set of 89 cardiovascular biomarkers. A single-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study using the human endotoxin model was performed. Ten healthy men were administered lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or placebo on two different study days after an overnight fast. Eighty-nine different cardiovascular biomarkers were measured repetitively over 48 h. Out of 89 cardiovascular biomarkers, 54 markers were significantly influenced by LPS infusion. The observed biomarker response to inflammation was more pronounced and complex than anticipated. In conclusion, our data show that the cardiovascular system is under enormous distress in response to experimental low-dose inflammation in humans, as demonstrated by a significant effect on 54 of the 89 biomarkers tested.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cardiovascular; Human endotoxin model; Infection lipopolysaccharide (LPS); Inflammation; Proximity extension assay (PEA).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Corrales-Medina VF, Alvarez KN, Weissfeld LA, Angus DC, Chirinos JA, Chang CC, Newman A, Loehr L, Folsom AR, Elkind MS, Lyles MF, Kronmal RA, Yende S. Association between hospitalization for pneumonia and subsequent risk of cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2015;313(3):264–274. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.18229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

