Clinical applications for exosomes: Are we there yet?
- PMID: 33751579
- PMCID: PMC8432553
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15432
Clinical applications for exosomes: Are we there yet?
Abstract
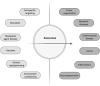
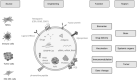
Exosomes are a subset of extracellular vesicles essential for cell-cell communication in health and disease with the ability to transport nucleic acids, functional proteins and other metabolites. Their clinical use as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic carriers has become a major field of research over recent years, generating rapidly expanding scientific interest and financial investment. Their reduced immunogenicity compared to liposomes or viral vectors and their ability to cross major physiological barriers like the blood-brain barrier make them an appealing and innovative option as biomarkers and therapeutic agents. Here, we review the latest clinical developments of exosome biotechnology for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, including the most recent COVID-19-related exosome-based clinical trials. We present current exosome engineering strategies for optimal clinical safety and efficacy, and assess the technology developed for good manufacturing practice compliant scaling up and storage approaches along with their limitations in pharmaceutical industry.
Keywords: cancer; exosome; immunomodulation; infectious diseases; inflammation; manufacturing; therapeutics.
© 2021 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are partially funded by a United Kingdom Research Council Innovate UK Biomedical Catalyst award (14720) awarded jointly with Evox Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander, S. P. H., Cidlowski, J. A., Kelly, E., Mathie, A., Peters, J. A., Veale, E. L., Armstrong, J. F., Faccenda, E., Harding, S. D., Pawson, A. J., Sharman, J. L., Southan, C., Davies, J. A., & GTP collaborators . (2019). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2019/2020: Nuclear hormones receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176, S229–S246. 10.1111/bph.14748 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez‐Erviti, L., Couch, Y., Richardson, J., Cooper, J. M., & Wood, M. J. (2011). Alpha‐synuclein release by neurons activates the inflammatory response in a microglial cell line. Neuroscience Research, 69(4), 337–342. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez‐Erviti, L., Seow, Y., Yin, H., Betts, C., Lakhal, S., & Wood, M. J. (2011). Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nature Biotechnology, 29(4), 341–345. - PubMed
-
- Andaloussi, S. E., Mäger, I., Breakefield, X. O., & Wood, M. J. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 12(5), 347–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

