Melatonin and its protective role in attenuating warm or cold hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 33751704
- PMCID: PMC8016647
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13021
Melatonin and its protective role in attenuating warm or cold hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
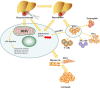
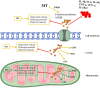
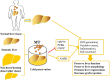
Although the liver is the only organ with regenerative capacity, various injury factors induce irreversible liver dysfunction and end-stage liver disease. Liver resection and liver transplantation (LT) are effective treatments for individuals with liver failure, liver cirrhosis and liver cancers. The remnant or transplanted liver tissues will undergo hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion (IR), which leads to oxidative stress, inflammation, immune injury and liver damage. Moreover, systemic ischaemia induced by trauma, stroke, myocardial ischaemia, haemorrhagic shock and other injury factors also induces liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) in individuals. Hepatic IRI can be divided into warm IRI, which is induced by liver surgery and systemic ischaemia, and cold IRI, which is induced by LT. Multiple studies have shown that melatonin (MT) acts as an endogenous free radical scavenger with antioxidant capacity and is also able to attenuate hepatic IRI via its anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic capacities. In this review, we discuss the potential mechanisms and current strategies of MT administration in liver surgery for protecting against warm or cold hepatic IRI. We highlight strategies to improve the efficacy and safety of MT for attenuating hepatic IRI in different conditions. After the potential mechanisms underlying the interactions between MT and other important cellular processes during hepatic IR are clarified, more opportunities will be available to use MT to treat liver diseases in the future.
Keywords: inflammation; injury; ischaemia/reperfusion; liver; melatonin; mitochondria.
© 2021 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of autophagy protects against liver injury in liver surgery-induced ischaemia/reperfusion.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(21):9905-9917. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16943. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34626066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detrimental effects of prolonged warm renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury are abrogated by supplemental hydrogen sulphide: an analysis using real-time intravital microscopy and polymerase chain reaction.BJU Int. 2012 Dec;110(11 Pt C):E1218-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11555.x. Epub 2012 Oct 9. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 23046222
-
Melatonin attenuates lung ischaemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018 May 1;26(5):761-767. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivx440. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29346581
-
Hepatic 31 P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy identified the impact of melatonin-pretreated mitochondria in acute liver ischaemia-reperfusion injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):10088-10099. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15617. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32691975 Free PMC article.
-
A review of melatonin in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury and clinical liver disease.Ann Med. 2014 Nov;46(7):503-11. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2014.934275. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Ann Med. 2014. PMID: 25033992 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative analyses of genes related to liver ischemia reperfusion injury.Hereditas. 2022 Oct 18;159(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00255-8. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 36253874 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay Between Inflammatory-immune and Interleukin-17 Signalings Plays a Cardinal Role on Liver Ischemia-reperfusion Injury-Synergic Effect of IL-17Ab, Tacrolimus and ADMSCs on Rescuing the Liver Damage.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Nov;19(8):2852-2868. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10611-4. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37632641
-
Engineered Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Therapeutics.Biomater Res. 2025 May 23;29:0212. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0212. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40416938 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of Preservative Fluids with Antioxidants in Terms of Their Efficacy in Liver Protection before Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 3;25(3):1850. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031850. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the immune system in liver transplantation and its implications for therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 13;4(6):e444. doi: 10.1002/mco2.444. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38098611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li J, Li RJ, Lv GY, et al. The mechanisms and strategies to protect from hepatic ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19:2036‐2047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

