Can ozone inactivate SARS-CoV-2? A review of mechanisms and performance on viruses
- PMID: 33752085
- PMCID: PMC7955572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125658
Can ozone inactivate SARS-CoV-2? A review of mechanisms and performance on viruses
Abstract
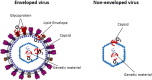
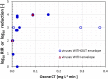
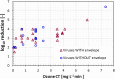
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic has challenged societies around the globe. Technologies based on ozone, a powerful oxidant, have been evaluated to inactivate this virus in aerosols and fomites. However, the high data diversity hinders the possibility of establishing a common ground for determining best practices for the use of these technologies. Furthermore, there is a lack of consensus regarding which are the main mechanisms of ozone virus inactivation. This critical review examined the most relevant information available regarding ozone application in gas-phase for different viruses inactivation (including recent publications dealing with SARS-CoV-2), and pointed towards envelope alteration as the main reaction pathway for enveloped viruses, such as is the case of SARS-CoV-2. It could also be concluded that gaseous ozone can be indeed an effective disinfectant, successfully inactivating viruses such us influenza A H1N1, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1 or even SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols or fomites. In reviewed works, low ozone exposures, just around 0.1-0.4 mg L-1 min, achieve about 4 log10 of inactivation in aerosols, while exposures between 1 and 4 mg L-1 min may be needed to guarantee an inactivation of 3-4 log10 in different fomites. Although further studies are required, ozone is an effective candidate to be used against SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses in surfaces and indoor locations.
Keywords: Aerosols; COVID-19; Enveloped viruses; Fomites; Inactivation; Ozonation; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alimohammadi M., Naderi M. Effectiveness of ozone gas on airborne virus inactivation in enclosed spaces: a review study. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1080/01919512.2020.1822149. - DOI
-
- Arévalo Camargo J., Murray K., Warriner K., Lubitz W. Characterization of efficacy and flow in a commercial scale forced air ozone reactor for decontamination of apples. LWT. 2019;113 doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108325. - DOI
-
- Blanchard E.L., Lawrence J.D., Noble J.A., Xu M., Joo T., Ng N.L., Schmidt B.E., Santangelo P.J., Finn M.G.G. Enveloped virus inactivation on personal protective equipment by exposure to ozone. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.05.23.20111435. 2020.05.23.20111435. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

