Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and retropharyngeal edema: A case series
- PMID: 33752089
- PMCID: PMC7931672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.110667
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and retropharyngeal edema: A case series
Abstract
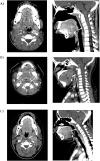
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is thought to follow SARS-CoV-2 infection and presents with fever and multisystem dysfunction. We report three children with suspected MIS-C found to have retropharyngeal edema without evidence of a bacterial etiology. We raise the possibility that an association between MIS-C and retropharyngeal edema exists.
Keywords: COVID-19; MIS-C; Retropharyngeal edema; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Emergency preparedness and response: multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Health Advisory. 2020 https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2020/han00432.asp
-
- Hoang J.K., Branstetter B.F., Eastwood J.D., et al. Multiplanar CT and MRI of collections in the retropharyngeal space: is it an abscess? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011;196(4):W426–W432. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous