Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
- PMID: 33752274
- PMCID: PMC8024148
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0206
Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade are reported to affect the clinical course of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM).
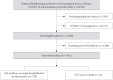
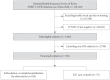
Methods: As of May 2020, analysis was conducted on all subjects who could confirm their history of claims related to COVID-19 in the National Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) database in Korea. Using this dataset, we compared the short-term prognosis of COVID-19 infection according to the use of DPP-4i and RAS blockade. Additionally, we validated the results using the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) of Korea dataset.
Results: Totally, data of 67,850 subjects were accessible in the HIRA dataset. Of these, 5,080 were confirmed COVID-19. Among these, 832 subjects with DM were selected for analysis in this study. Among the subjects, 263 (31.6%) and 327 (39.3%) were DPP4i and RAS blockade users, respectively. Thirty-four subjects (4.09%) received intensive care or died. The adjusted odds ratio for severe treatment among DPP-4i users was 0.362 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.135 to 0.971), and that for RAS blockade users was 0.599 (95% CI, 0.251 to 1.431). These findings were consistent with the analysis based on the NHIS data using 704 final subjects. The adjusted odds ratio for severe treatment among DPP-4i users was 0.303 (95% CI, 0.135 to 0.682), and that for RAS blockade users was 0.811 (95% CI, 0.391 to 1.682).
Conclusion: This study suggests that DPP-4i is significantly associated with a better clinical outcome of patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19; COVID-19 drug treatment; Diabetes mellitus; Dipeptidyl peptidase 4.
Conflict of interest statement
Researchers from a pharmaceutical company participated in this study (Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, and Dae-Sung Kyoung). They are experts on claims data, and their institutions have not intentionally influenced the basic hypothesis of the study, analysis plan, result arrangement, result interpretation, and manuscript preparation. The researchers from other institutions have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:251-9).Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Jul;45(4):615-616. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0081. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 34352990 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:251-9).Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Jul;45(4):619-620. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0118. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 34352992 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

