PVT1 Expression Is a Predictor for Poor Survival of Prostate Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33752525
- PMCID: PMC8093616
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033820971610
PVT1 Expression Is a Predictor for Poor Survival of Prostate Cancer Patients
Abstract
Objective: Dysregulation of long noncoding RNA is associated with a variety of cancers and LncRNA has anticancer or carcinogenic activities. PVT1, as a long noncoding RNA, plays an important role in the development of cancer.
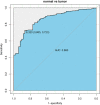
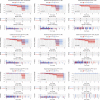
Methods: We use R to download and analyze the data in TCGA database. ROC curve is generated to evaluate the significance of PVT1 expression for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Chi-square test is used to test correlation between PVT1 expression and clinical pathological features. Survival curve and univariate and multivariate cox regression analysis is performed to compare differences in the effect on the survival rate between PVT1 high expression and low expression.
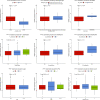
Results: The expression of PTV1 in tumor tissues was significantly higher than that in normal tissues(P<2.2e-16). The difference of PTV1 expression was observed according to vital status (P = 0.0051) and Gleason score (P = 0.0012). The expression of PTV1 is significantly associated with T classification (P < 0.0001), N classification (P = 0.0499), PSA (P = 0.0001), Gleason Score (P < 0.0001), targeted molecular therapy (P = 0.0264) and vital status(P = 0.0036). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.860, which revealed PTV1 expression has excellent diagnostic value in prostate cancer. Patients with high PVT1 expression had a worse prognosis.
Conclusions: PVT1 expression may be a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer.
Keywords: PVT1; biomarker; diagnosis; prognosis; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Litwin MS, Tan HJ. The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer a review. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2532–2542. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.7248 - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA-Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. doi:10.3322/caac.21551 - PubMed
-
- Malouff TD, Stross WC, Seneviratne DS, et al. Current use of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lowand intermediate risk prostate cancer: a national cancer database analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020;23(2):349–355. - PubMed
-
- Zelefsky MJ, Eastham JA, Cronin AM, et al. Metastasis after radical prostatectomy or external beam radiotherapy for patients with clinically localized prostate cancer: a comparison of clinical cohorts adjusted for case mix. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(9):1508–1513. doi:10.1200/Jco.2009.22.2265 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

