Risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation in the gallbladder are closely related to lipid metabolism
- PMID: 33752687
- PMCID: PMC7983281
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-021-01452-6
Risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation in the gallbladder are closely related to lipid metabolism
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to assess the risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation in the gallbladder.
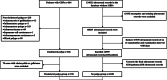
Methods: This was a multicenter retrospective study based on pathology. From January 2016 to December 2019, patients who underwent cholecystectomy and non-polyp participants confirmed by continuous ultrasound follow-ups were reviewed. Patients in the cholesterol polyp group were recruited from three high-volume centers with a diagnosis of pathologically confirmed cholesterol polyps larger than 10 mm. Population characteristics and medical data were collected within 24 h of admission before surgery. The non-polyp group included participants from the hospital physical examination center database. They had at least two ultrasound examinations with an interval longer than 180 days. Data from the final follow-up of the non-polyp group were analyzed. The risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation were analyzed by comparing the two groups.
Results: A total of 4714 participants were recruited, including 376 cholesterol polyp patients and 4338 non-polyp participants. In univariate analysis, clinical risk factors for cholesterol polyps were age, male sex, higher body mass index (BMI), higher low-density lipoprotein (LDL), lower high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and higher aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. In multivariate logistic analysis, independent risk factors were age > 50 years (odds ratio [OR] = 3.02, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.33-3.91, P < 0.001], LDL > 2.89 mmol/L (OR = 1.38, 95% CI 1.08-1.78, P = 0.011), lower HDL (OR = 1.78 95% CI 1.32-2.44, P < 0.001), AST > 40 IU/L (OR = 3.55, 95% CI 2.07-6.07, P < 0.001), and BMI > 25 kg/m 2 (OR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.01-1.72, P = 0.037).
Conclusions: Age, LDL, HDL, AST, and BMI are strong risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation. Older overweight patients with polyps, accompanied by abnormal lipid levels, are at high risk for cholesterol polyps.
Keywords: Cholesterol polyps; Formation; Gallbladder; Lipid metabolism; Multicenter; Pathology; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of prediction model in distinguishing gallbladder adenoma from cholesterol polyp.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Oct;37(10):1893-1900. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15928. Epub 2022 Jul 22. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35750491
-
Association between the non-HDL-cholesterol-to-HDL-cholesterol ratio and the risk of gallbladder polyp formation among men: a retrospective cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jun 23;19(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01322-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32576257 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Ultrasound Assessment of Changes in Size and Number of Incidentally Detected Gallbladder Polyps.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022 Mar;218(3):472-483. doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.26614. Epub 2021 Sep 22. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022. PMID: 34549608
-
Risk factors of gallbladder polyps formation in East Asian population: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Asian J Surg. 2020 Jan;43(1):52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2019.03.015. Epub 2019 May 17. Asian J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31109764
-
[Cholesterol polyp].Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu. 1996;(9):280-2. Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu. 1996. PMID: 8705477 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Differences in the Impact of Obesity and Metabolic Unhealthiness on the Risk of Gallbladder Polyp.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Nov;64(11):658-664. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0182. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 37880846 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hepatitis B virus infection on the risk of gallbladder polyps: a cohort study.Korean J Intern Med. 2023 Nov;38(6):844-853. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2023.197. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Korean J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37848340 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Study of the Prevalence and Associated Factors of Gallbladder Polyps among Residents of Two Korean Cities.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 15;13(8):2290. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082290. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673563 Free PMC article.
-
Gallbladder polypoid lesions: Current practices and future prospects.Chin Med J (Engl). 2024 Jul 20;137(14):1674-1683. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003019. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024. PMID: 38420780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing a radiomics model using contrast-enhanced ultrasound for preoperative prediction of neoplastic gallbladder polyps exceeding 10 mm.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 3;30(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02292-1. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39901203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen CY, Lu CL, Chang FY, Lee SD. Risk factors for gallbladder polyps in the Chinese population. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(11):2066–2068. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical