Inhibition of TLR4 signaling protects mice from sensory and motor dysfunction in an animal model of autoimmune peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 33752705
- PMCID: PMC7983271
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02126-x
Inhibition of TLR4 signaling protects mice from sensory and motor dysfunction in an animal model of autoimmune peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
Background: While the etiology remains elusive, macrophages and T cells in peripheral nerves are considered as effector cells mediating autoimmune peripheral neuropathy (APN), such as Guillain-Barre syndrome. By recognizing both pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) signals, TLRs play a central role in the initiation of both innate and adaptive immune responses. In this study, we aimed to understand the involvement of TLR4 in the pathogenesis of APN and explore the potential of TLR4 as a drug target for therapeutic use.
Methods: APN was induced by a partial ligation on one of the sciatic nerves in B7.2 (L31) transgenic mice which possess a predisposed inflammatory background. APN pathology and neurological function were evaluated on the other non-injured sciatic nerve.
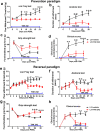
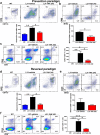
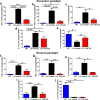
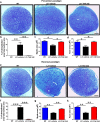
Results: TLR4 and its endogenous ligand HMGB1 were highly expressed in L31 mice, in circulating immune cells and in peripheral nerves. Enhanced TLR4 signaling was blocked with TAK 242, a selective TLR4 inhibitor, before and after disease onset. Intraperitoneal administration of TAK 242 not only inhibited monocyte, macrophage and CD8+ T cell activation, but also reduced the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. TAK 242 protected mice from severe myelin and axonal loss, resulting in a remarkable improvement in mouse motor and sensory functions. TAK 242 was effective in alleviating the disease in both preventive and reversal paradigms.
Conclusion: The study identified the critical contribution of TLR4-mediated macrophage activation in disease course and provided strong evidence to support TLR4 as a useful drug target for treating inflammatory autoimmune neuropathy.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; CD8+ T cells; DAMPs; Demyelination; Inflammation; Macrophages; TLR4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

