Time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography reveals early structural changes in channelrhodopsin
- PMID: 33752801
- PMCID: PMC7987342
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.62389
Time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography reveals early structural changes in channelrhodopsin
Abstract
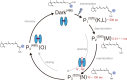
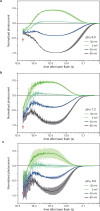
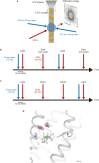
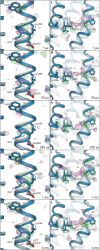
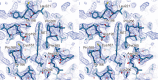
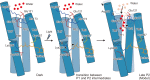
Channelrhodopsins (ChRs) are microbial light-gated ion channels utilized in optogenetics to control neural activity with light . Light absorption causes retinal chromophore isomerization and subsequent protein conformational changes visualized as optically distinguished intermediates, coupled with channel opening and closing. However, the detailed molecular events underlying channel gating remain unknown. We performed time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallographic analyses of ChR by using an X-ray free electron laser, which revealed conformational changes following photoactivation. The isomerized retinal adopts a twisted conformation and shifts toward the putative internal proton donor residues, consequently inducing an outward shift of TM3, as well as a local deformation in TM7. These early conformational changes in the pore-forming helices should be the triggers that lead to opening of the ion conducting pore.
Keywords: C1C2; Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; channelrhodopsin; chlamydomonas reinhardtii; molecular biophysics; structural biology.
© 2021, Oda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KO, TN, TN, KY, KI, SI, JV, KH, AM, KK, TI, II, TI, RU, RE, SO, GK, TK, TK, WS, HS, TT, MT, RT, AT, RN, MF, HM, YL, EN, RT, TT, MS, TK, TS, TF, YY, SO, YJ, KT, RI, SH, HK, PH, SI, MK, TN, ON No competing interests declared
Figures












References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 16H06294/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 18J21256/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 17H05000/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JPMJPR14L9/Japan Science and Technology Agency
- JPMJPR14L8/Japan Science and Technology Agency
- Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery andLife Science Research (Basis for Supporting Innovative Drug Discovery and Life Science Research(BINDS))/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- SFB1078 (B2)/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- UniCat/Cluster of Excellence in Inflammation Research
- BIG-NSE/Cluster of Excellence in Inflammation Research
- E4/Cluster of Excellence in Inflammation Research
- SPP 1926/Cluster of Excellence in Inflammation Research
- ERC-2016-StG 714762/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- Senior Research Professor/Hertie Foundation
- X-ray Free-Electron Laser Priority Strategy Program/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

