Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 33752856
- PMCID: PMC7995616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2020.11.010
Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
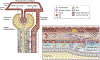
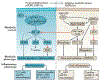
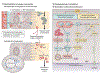
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is a common and life-threatening complication in hospitalized and critically ill patients. It is characterized by rapid deterioration of renal function associated with sepsis. The pathophysiology of S-AKI remains incompletely understood, so most therapies remain reactive and nonspecific. Possible pathogenic mechanisms to explain S-AKI include microcirculatory dysfunction, a dysregulated inflammatory response, and cellular metabolic reprogramming. In addition, several biomarkers have been developed in an attempt to improve diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of S-AKI. This article discusses the current understanding of S-AKI, recent advances in pathophysiology and biomarker development, and current preventive and therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: AKI; Biomarkers; Inflammation; Metabolic reprogramming; Microcirculation; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure H. Gomez received a research grant from TES pharma to study mechanisms of AKI in sepsis, and is site principal investigator of an industry-sponsored grant (AM Pharma) to study the effect of recombinant alkaline phosphatase in sepsis-induced AKI.
Figures

References
-
- Coca SG, Yusuf B, Shlipak MG, Garg AX & Parikh CR Long-term risk of mortality and other adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. American journal of kidney diseases : the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation 53, 961–973, doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.11.034 (2009). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

