Left pneumonectomy for primary lung cancer with Trousseau's syndrome
- PMID: 33753389
- PMCID: PMC7986757
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-240927
Left pneumonectomy for primary lung cancer with Trousseau's syndrome
Abstract
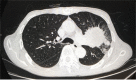
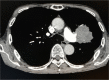
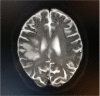
Trousseau's syndrome is a paraneoplastic syndrome and a pathological condition that causes cerebral stroke symptoms due to hypercoagulation associated with malignant tumours. There have been many cases of advanced lung cancer, but few reports have described surgery for lung cancer with Trousseau's syndrome. We encountered a 76-year-old man suspected of having Trousseau's syndrome associated with lung cancer. He was transferred to our hospital on the second day after the onset. After admission, he was treated with heparin and edaravone, and his condition improved. On the 12th day after the onset, we performed left pneumonectomy and lymph node dissection (ND2a-2). The final pathological results were adenocarcinoma, pathological stage was T4 (tumour size: 77 mm, pulmonary artery invasion) N1(#11, #12u) M0, stage IIIA. He has been recurrence free for 23 months since the surgery. In the future, we need to follow his condition carefully.
Keywords: cardiothoracic surgery; lung cancer (oncology); surgery.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Trousseau A. Phlegmasia alba dolens. Clinique Medicale de l’Hotel Dieu de Paris, Vol 3. Paris: Bailliere, 1865: 654–712.
-
- Sack GH, Levin J, Bell WR. Trousseau's syndrome and other manifestations of chronic disseminated coagulopathy in patients with neoplasms: clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic features. Medicine 1977;56:1–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
