Roles of OmpX, an Outer Membrane Protein, on Virulence and Flagellar Expression in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 33753414
- PMCID: PMC8316124
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00721-20
Roles of OmpX, an Outer Membrane Protein, on Virulence and Flagellar Expression in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
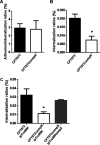
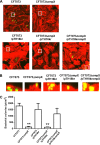
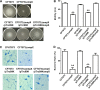
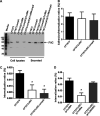
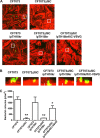
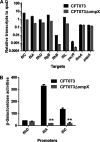
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) is a major pathogen that causes urinary tract infection (UTI). This bacterium adheres to and internalizes within urinary tract cells, where it aggregates and subsequently forms biofilm-like multicellular colonies that protect UPEC from antimicrobial agents and the host's immune system. Here, we show that OmpX, an outer membrane protein, plays a role in the pathogenesis of UPEC in renal cells. Deletion of ompX decreased bacterial internalization and aggregation within kidney epithelial cells and also impaired the colonization of mouse urinary tracts, but the ompX mutant still adhered to the epithelial cells at a level similar to that of the parent strain. FlhD, the master regulator of flagellum-related genes, had a low expression level in the ompX mutant compared to the parent strain, and the ompX mutant exhibited defective motility due to lower flagellar production than the parent strain. The fliC mutant, which lacks flagella, exhibited lower levels of bacterial internalization and aggregation than the parent strain. Additional deletion of ompX in the fliC mutant did not further decrease bacterial internalization. These combined results suggest that OmpX contributes to flagellar production in UPEC and then sustains UPEC virulence associated with bacterial internalization and aggregation within urinary tract cells and colonization in the urinary tract.
Keywords: biofilm; flagella; gene regulation; motility; pathogenesis; pyelonephritis; urinary tract infection; virulence.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Iron limitation induces motility in uropathogenic E. coli CFT073 partially through action of LpdA.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0104824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01048-24. Epub 2024 Jun 14. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38874412 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of CytR, an anti-activator of cyclic-AMP receptor protein (CRP) on flagellar expression and virulence in uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jan 15;521(3):555-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.165. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31677792
-
Discovery of New Genes Involved in Curli Production by a Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strain from the Highly Virulent O45:K1:H7 Lineage.mBio. 2018 Aug 21;9(4):e01462-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01462-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30131362 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence and Fitness Determinants of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Aug;3(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.UTI-0015-2012. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.UTI-0015-2012. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26350328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns, and the correlation between biofilm formation with virulence factors in uropathogenic E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections.Microb Pathog. 2020 Jul;144:104196. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104196. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32283258
Cited by
-
SurA-like and Skp-like Proteins as Important Virulence Determinants of the Gram Negative Bacterial Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 24;24(1):295. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010295. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adsorption of extracellular proteases and pyocyanin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa using a macroporous magnesium oxide-templated carbon decreases cytotoxicity.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2022 Aug 18;3:100160. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.100160. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2022. PMID: 36518171 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-driven lung TRM cells provide immunity against Klebsiella via fibroblast IL-17R signaling.Sci Immunol. 2021 Sep 10;6(63):eabf1198. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf1198. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Sci Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34516780 Free PMC article.
-
TusDCB, a sulfur transferase complex involved in tRNA modification, contributes to UPEC pathogenicity.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 18;14(1):8978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59614-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38637685 Free PMC article.
-
Role of GuaB, the inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase of uropathogenic Escherichia coli pathogenicity: a key factor for bladder infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 5;13(8):e0022125. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00221-25. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40525840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayami H, Takahashi S, Ishikawa K, Yasuda M, Yamamoto S, Wada K, Kobayashi K, Hamasuna R, Minamitani S, Matsumoto T, Kiyota H, Tateda K, Sato J, Hanaki H, Masumori N, Nishiyama H, Miyazaki J, Fujimoto K, Tanaka K, Uehara S, Matsubara A, Ito K, Hayashi K, Kurimura Y, Ito S, Takeuchi T, Narita H, Izumitani M, Nishimura H, Kawahara M, Hara M, Hosobe T, Takashima K, Chokyu H, Matsumura M, Ihara H, Uno S, Monden K, Sumii T, Kawai S, Kariya S, Sato T, Yoshioka M, Kadena H, Matsushita S, Nishi S, Hosokawa Y, Shirane T, Yoh M, Watanabe S, et al.. 2019. Second nationwide surveillance of bacterial pathogens in patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis conducted by Japanese Surveillance Committee from 2015 to 2016: antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Chemother 25:413–422. 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.02.021. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

