Long-term outcomes after endoscopic treatment for Barrett's neoplasia with radiofrequency ablation ± endoscopic resection: results from the national Dutch database in a 10-year period
- PMID: 33753417
- PMCID: PMC8762001
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322615
Long-term outcomes after endoscopic treatment for Barrett's neoplasia with radiofrequency ablation ± endoscopic resection: results from the national Dutch database in a 10-year period
Abstract
Objective: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)±endoscopic resection (ER) is the preferred treatment for early neoplasia in Barrett's oesophagus (BE). We aimed to report short-term and long-term outcomes for all 1384 patients treated in the Netherlands (NL) from 2008 to 2018, with uniform treatment and follow-up (FU) in a centralised setting.
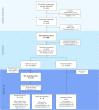
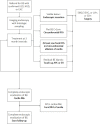
Design: Endoscopic therapy for early BE neoplasia in NL is centralised in nine expert centres with specifically trained endoscopists and pathologists that adhere to a joint protocol. Prospectively collected data are registered in a uniform database. Patients with low/high-grade dysplasia or low-risk cancer, were treated by ER of visible lesions followed by trimonthly RFA sessions of any residual BE until complete eradication of BE (CE-BE). Patients with ER alone were not included.
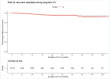
Results: After ER (62% of cases; 43% low-risk cancers) and median 1 circumferential and 2 focal RFA (p25-p75 0-1; 1-2) per patient, CE-BE was achieved in 94% (1270/1348). Adverse events occurred in 21% (268/1386), most commonly oesophageal stenosis (15%), all were managed endoscopically. A total of 1154 patients with CE-BE were analysed for long-term outcomes. During median 43 months (22-69) and 4 endoscopies (1-5), 38 patients developed dysplastic recurrence (3%, annual recurrence risk 1%), all were detected as endoscopically visible abnormalities. Random biopsies from a normal appearing cardia showed intestinal metaplasia (IM) in 14% and neoplasia in 0%. A finding of IM in the cardia was reproduced during further FU in only 33%, none progressed to neoplasia. Frequent FU visits in the first year of FU were not associated with recurrence risk.
Conclusion: In a setting of centralised care, RFA±ER is effective for eradication of Barrett's related neoplasia and has remarkably low rates of dysplastic recurrence. Our data support more lenient FU intervals, with emphasis on careful endoscopic inspection. Random biopsies from neosquamous epithelium and cardia are of questionable value.
Netherlands trial register number: NL7039.
Keywords: Barrett's carcinoma; Barrett's oesophagus; endoscopic procedures.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SvM, EN, AH, AB, AA, BES, EJS, WC, ADK, SEMvdV, PJFdJ, TJT, WBN, FTMP, JW, MHMGH, REP declared to have no disclosures relevant to this manuscript. BLAMW received financial support for IRB-approved research from C2Therapeutics/Pentax Medical. JJGHMB received financial support for IRB-approved research from C2Therapeutics/Pentax Medical, Medtronic, and Aqua Medical.
Figures
Comment in
-
Location and appearance of dysplastic Barrett's esophagus recurrence after endoscopic eradication therapy: no additional yield from random biopsy sampling neosquamous mucosa.Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Nov;98(5):722-732. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37301519
References
-
- Gastroenterologists DSo . Richtlijn Barrett-Oesofagus, 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
