Multiple migrations to the Philippines during the last 50,000 years
- PMID: 33753512
- PMCID: PMC8020671
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2026132118
Multiple migrations to the Philippines during the last 50,000 years
Abstract
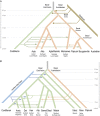
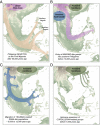
Island Southeast Asia has recently produced several surprises regarding human history, but the region's complex demography remains poorly understood. Here, we report ∼2.3 million genotypes from 1,028 individuals representing 115 indigenous Philippine populations and genome-sequence data from two ∼8,000-y-old individuals from Liangdao in the Taiwan Strait. We show that the Philippine islands were populated by at least five waves of human migration: initially by Northern and Southern Negritos (distantly related to Australian and Papuan groups), followed by Manobo, Sama, Papuan, and Cordilleran-related populations. The ancestors of Cordillerans diverged from indigenous peoples of Taiwan at least ∼8,000 y ago, prior to the arrival of paddy field rice agriculture in the Philippines ∼2,500 y ago, where some of their descendants remain to be the least admixed East Asian groups carrying an ancestry shared by all Austronesian-speaking populations. These observations contradict an exclusive "out-of-Taiwan" model of farming-language-people dispersal within the last four millennia for the Philippines and Island Southeast Asia. Sama-related ethnic groups of southwestern Philippines additionally experienced some minimal South Asian gene flow starting ∼1,000 y ago. Lastly, only a few lowlanders, accounting for <1% of all individuals, presented a low level of West Eurasian admixture, indicating a limited genetic legacy of Spanish colonization in the Philippines. Altogether, our findings reveal a multilayered history of the Philippines, which served as a crucial gateway for the movement of people that ultimately changed the genetic landscape of the Asia-Pacific region.
Keywords: Austronesian; ISEA; Negrito; Philippines; human population genetics.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Détroit F., et al., A new species of Homo from the Late Pleistocene of the Philippines. Nature 568, 181–186 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Mijares A. S., et al., New evidence for a 67,000-year-old human presence at Callao Cave, Luzon, Philippines. J. Hum. Evol. 59, 123–132 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Reid L. A., Who are the Philippine negritos? Evidence from language. Hum. Biol. 85, 329–358 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

