EVI1 dysregulation: impact on biology and therapy of myeloid malignancies
- PMID: 33753715
- PMCID: PMC7985498
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-021-00457-9
EVI1 dysregulation: impact on biology and therapy of myeloid malignancies
Abstract
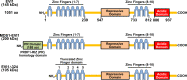
Ecotropic viral integration site 1 (Evi1) was discovered in 1988 as a common site of ecotropic viral integration resulting in myeloid malignancies in mice. EVI1 is an oncogenic zinc-finger transcription factor whose overexpression contributes to disease progression and an aggressive phenotype, correlating with poor clinical outcome in myeloid malignancies. Despite progress in understanding the biology of EVI1 dysregulation, significant improvements in therapeutic outcome remain elusive. Here, we highlight advances in understanding EVI1 biology and discuss how this new knowledge informs development of novel therapeutic interventions. EVI1 is overexpression is correlated with poor outcome in some epithelial cancers. However, the focus of this review is the genetic lesions, biology, and current therapeutics of myeloid malignancies overexpressing EVI1.
Conflict of interest statement
T.M.K. receives research funding from BMS/Celgene, Amgen, AstraZaneca, Astellas, Pfizer, AbbVie, Genentech, JAZZ, Cellenkos, InCyte, and Ascentage; T.M.K. serves as a consultant/advisory board member for Agios, Pfizer, Abbvie, Genentech, JAZZ, Daiichi Sankyo and Novartis. C.D.D. receives research funding from Abbvie, Agios, Calithera, Cleave, BMS/Celgene, Daiichi-Sankyo, ImmuneOnc and Loxo. C.D.D. serves as a consultant to Abbvie, Agios, Celgene/BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, ImmuneOnc, Novartis, and Takeda. C.D.D. serves on an advisory board with stock options for Notable Labs. K.N.B. serves as a consultant to Iterion Therapeutics. All other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Morishita K, et al. The human Evi-1 gene is located on chromosome 3q24-q28 but is not rearranged in three cases of acute nonlymphocytic leukemias containing t(3;5)(q25;q34) translocations. Oncogene Res. 1990;5:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Bordereaux D, Fichelson S, Tambourin P, Gisselbrecht S. Alternative splicing of the Evi-1 zinc finger gene generates mRNAs which differ by the number of zinc finger motifs. Oncogene. 1990;5:925–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

