The adipokine Retnla deficiency increases responsiveness to cardiac repair through adiponectin-rich bone marrow cells
- PMID: 33753732
- PMCID: PMC7985519
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03593-z
The adipokine Retnla deficiency increases responsiveness to cardiac repair through adiponectin-rich bone marrow cells
Abstract
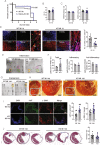
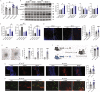
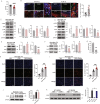
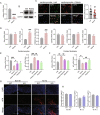
Resistin-like alpha (Retnla) is a member of the resistin family and known to modulate fibrosis and inflammation. Here, we investigated the role of Retnla in the cardiac injury model. Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced in wild type (WT), Retnla knockout (KO), and Retnla transgenic (TG) mice. Cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography and was significantly preserved in the KO mice, while worsened in the TG group. Angiogenesis was substantially increased in the KO mice, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis was markedly suppressed in the KO mice. By Retnla treatment, the expression of p21 and the ratio of Bax to Bcl2 were increased in cardiomyocytes, while decreased in cardiac fibroblasts. Interestingly, the numbers of cardiac macrophages and unsorted bone marrow cells (UBCs) were higher in the KO mice than in the WT mice. Besides, phosphorylated histone H3(+) cells were more frequent in bone marrow of KO mice. Moreover, adiponectin in UBCs was notably higher in the KO mice compared with WT mice. In an adoptive transfer study, UBCs were isolated from KO mice to transplant to the WT infarcted heart. Cardiac function was better in the KO-UBCs transplanted group in the WT-UBCs transplanted group. Taken together, proliferative and adiponectin-rich bone marrow niche was associated with substantial cardiac recovery by suppression of cardiac apoptosis and proliferation of cardiac fibroblast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-arrestin2 in infiltrated macrophages inhibits excessive inflammation after myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 8;8(7):e68351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068351. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861891 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 5 regulates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 Jan 12;55(2):135-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.041. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20117381
-
EMC10 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Protein Complex Subunit 10) Is a Bone Marrow-Derived Angiogenic Growth Factor Promoting Tissue Repair After Myocardial Infarction.Circulation. 2017 Nov 7;136(19):1809-1823. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029980. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28931551
-
Adipolin/C1q/Tnf-related protein 12 prevents adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 4;15(12):e0243483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243483. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33275602 Free PMC article.
-
Retnla overexpression attenuates allergic inflammation of the airway.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 21;9(11):e112666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112666. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25415454 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-Induced Mitogenic Factor: A Multifunctional Protein Involved in Health and Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 15;9:691774. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.691774. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34336840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5 induces macrophage activation to promote renal fibrosis via Retnla.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2519815. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2519815. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40570826 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional changes during isoproterenol-induced cardiac fibrosis in mice.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 18;10:1263913. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1263913. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38178867 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

