R-split-EPOCH plus high dose methotrexate in untreated diffuse large B cell lymphoma with MYC rearrangement or double expression of MYC and BCL-2
- PMID: 33754004
- PMCID: PMC7974535
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.52958
R-split-EPOCH plus high dose methotrexate in untreated diffuse large B cell lymphoma with MYC rearrangement or double expression of MYC and BCL-2
Abstract
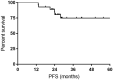
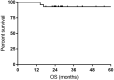
Purpose: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with MYC rearrangement or double expression of MYC and BCL-2 (DE DLBCL) has a relatively poor prognosis and does not respond well to standard R-CHOP. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of R-split-EPOCH plus high dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) in the particular patient population. Methods: A total of 28 patients diagnosed with DE DLBCL or DLBCL with MYC rearrangement between January 2015 and December 2018 were included and retrospectively analyzed. All the participants underwent R-split-EPOCH plus HD-MTX as introduction therapy, with split infusion of etoposide, doxorubicin, and vincristine for 48 hours on D1-2 and D10-11, respectively. Results: The overall objective response (ORR) rate was 100%, with 24 (85.7%) complete response (CR) and 4 (14.3%) partial response (PR). The CR rate was 76.9% and 93.3% for DLBCL patients with MYC rearrangement and DE DLBCL patients, respectively. The 1- and 3-year PFS rate was 100% and 74.9%, respectively. The 1- and 3-year OS rate was 100% and 92.9%, respectively. Grade 3/4 non-hematological toxicity and grade 3/4 hematological toxicity occurred in 50% and 85.7% of patients, respectively. No treatment-related death was reported. Conclusions: R-split-EPOCH plus HD-MTX regimen is an effective and feasible treatment option for DE DLBCL and DLBCL with MYC rearrangement.
Keywords: MYC; R-split-EPOCH; diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL); double expression; high dose methotrexate (HD-MTX).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Cai Z, Liu Q. Understanding the Global Cancer Statistics 2018: implications for cancer control. Science China. Life sciences. 2019. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R. et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2002;346:235–42. - PubMed
-
- Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Fermé C. et al. Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:4117–26. - PubMed
-
- Pfreundschuh M, Kuhnt E, Trümper L, Osterborg A, Trneny M, Shepherd L. et al. CHOP-like chemotherapy with or without rituximab in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: 6-year results of an open-label randomised study of the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. The Lancet. Oncology. 2011;12:1013–22. - PubMed
-
- Savage KJ, Johnson NA, Ben-Neriah S, Connors JM, Sehn LH, Farinha P. et al. MYC gene rearrangements are associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy. Blood. 2009;114:3533–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials