The histone acetyltransferase HBO1 functions as a novel oncogenic gene in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 33754016
- PMCID: PMC7978299
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.55655
The histone acetyltransferase HBO1 functions as a novel oncogenic gene in osteosarcoma
Abstract
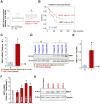
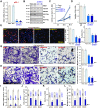
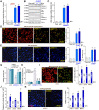
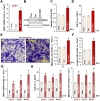
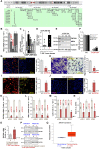
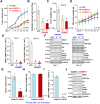
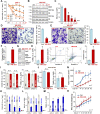
HBO1 (KAT7 or MYST2) is a histone acetyltransferase that acetylates H3 and H4 histones. Methods: HBO1 expression was tested in human OS tissues and cells. Genetic strategies, including shRNA, CRISPR/Cas9 and overexpression constructs, were applied to exogenously alter HBO1 expression in OS cells. The HBO1 inhibitor WM-3835 was utilized to block HBO1 activation. Results:HBO1 mRNA and protein expression is significantly elevated in OS tissues and cells. In established (MG63/U2OS lines) and primary human OS cells, shRNA-mediated HBO1 silencing and CRISPR/Cas9-induced HBO1 knockout were able to potently inhibit cell viability, growth, proliferation, as well as cell migration and invasion. Significant increase of apoptosis was detected in HBO1-silenced/knockout OS cells. Conversely, ectopic HBO1 overexpression promoted OS cell proliferation and migration. We identified ZNF384 (zinc finger protein 384) as a potential transcription factor of HBO1. Increased binding between ZNF384 and HBO1 promoter was detected in OS cell and tissues, whereas ZNF384 silencing via shRNA downregulated HBO1 and produced significant anti-OS cell activity. In vivo, intratumoral injection of HBO1 shRNA lentivirus silenced HBO1 and inhibited OS xenograft growth in mice. Furthermore, growth of HBO1-knockout OS xenografts was significantly slower than the control xenografts. WM-3835, a novel and high-specific small molecule HBO1 inhibitor, was able to potently suppressed OS cell proliferation and migration, and led to apoptosis activation. Furthermore, intraperitoneal injection of a single dose of WM-3835 potently inhibited OS xenograft growth in SCID mice. Conclusion: HBO1 overexpression promotes OS cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: HBO1; WM-3835; histone acetylation; osteosarcoma.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multifunctional acyltransferase HBO1: a key regulatory factor for cellular functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00661-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39543485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A first-in-class HBO1 inhibitor WM-3835 inhibits castration-resistant prostate cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jan 28;14(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05606-5. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36709328 Free PMC article.
-
HBO1 induces histone acetylation and is important for non-small cell lung cancer cell growth.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 May 9;18(8):3313-3323. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72526. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35637972 Free PMC article.
-
HBO1 overexpression is important for hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 26;12(6):549. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03818-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34039960 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering structure, function and mechanism of lysine acetyltransferase HBO1 in protein acetylation, transcription regulation, DNA replication and its oncogenic properties in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Feb;77(4):637-649. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03296-x. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31535175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TIMM44 is a potential therapeutic target of human glioma.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 31;12(17):7586-7602. doi: 10.7150/thno.78616. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438483 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional acyltransferase HBO1: a key regulatory factor for cellular functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00661-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39543485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and functional implications of YME1L in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 18;15(6):423. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06811-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38890304 Free PMC article.
-
ADCK1 is a potential therapeutic target of osteosarcoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 12;13(11):954. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05401-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36371387 Free PMC article.
-
A CIC-related-epigenetic factors-based model associated with prediction, the tumor microenvironment and drug sensitivity in osteosarcoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 15;14(1):1308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49770-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38225273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ, Thomas DM. Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:722–35. - PubMed
-
- Ottaviani G, Jaffe N. The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

