Distinct placental molecular processes associated with early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia
- PMID: 33754042
- PMCID: PMC7978310
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.56141
Distinct placental molecular processes associated with early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia
Abstract
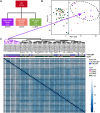
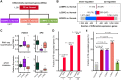
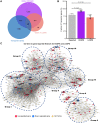
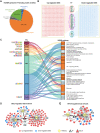
Background: Patients with preeclampsia display a spectrum of onset time and severity of clinical presentation, yet the underlying molecular bases for the early-onset and late-onset clinical subtypes are not known. Although several transcriptome studies have been done on placentae from PE patients, only a small number of differentially expressed genes have been identified due to very small sample sizes and no distinguishing of clinical subtypes. Methods: We carried out RNA-seq on 65 high-quality placenta samples, including 33 from 30 patients and 32 from 30 control subjects, to search for dysregulated genes and the molecular network and pathways they are involved in. Results: We identified two functionally distinct sets of dysregulated genes in the two major subtypes: 2,977 differentially expressed genes in early-onset severe preeclampsia, which are enriched with metabolism-related pathways, notably transporter functions; and 375 differentially expressed genes in late-onset severe preeclampsia, which are enriched with immune-related pathways. We also identified some key transcription factors, which may drive the widespread gene dysregulation in both early-onset and late-onset patients. Conclusion: These results suggest that early-onset and late-onset severe preeclampsia have different molecular mechanisms, whereas the late-onset mild preeclampsia may have no placenta-specific causal factors. A few regulators may be the key drivers of the dysregulated molecular pathways.
Keywords: clinical subtypes; molecular mechanism; placenta; preeclampsia; transcriptome.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Brown MA, Magee LA, Kenny LC, Karumanchi SA, McCarthy FP, Saito S. et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension. 2018;72:24–43. - PubMed
-
- Mol BWJ, Roberts CT, Thangaratinam S, Magee LA, de Groot CJM, Hofmeyr GJ. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2016;387:999–1011. - PubMed
-
- Raymond D, Peterson E. A critical review of early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2011;66:497–506. - PubMed
-
- Herzog EM, Eggink AJ, Reijnierse A, Kerkhof MA, de Krijger RR, Roks AJ. et al. Impact of early- and late-onset preeclampsia on features of placental and newborn vascular health. Placenta. 2017;49:72–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

